Customer Logins
Obtain the data you need to make the most informed decisions by accessing our extensive portfolio of information, analytics, and expertise. Sign in to the product or service center of your choice.
Customer Logins
BLOG
May 01, 2020
Coal, gas, or renewables: Electricity supply responding to lower demand during COVID-19
With countries going into lockdowns one by one, electricity demand around the world has been dropping. Power generation requirement has gone down with it, but how are different generation resources responding to the decline in load?
Last time the world's power systems witnessed significant demand weakness was during the financial crisis a decade ago. Ten years on, one major difference in power supply is the role of renewables. Wind, solar and other renewable technologies only accounted for 5% of the world's power generation capacity in 2009; that figure has increased to 18% by 2019. In some large renewable markets such as China, Europe and the United States, renewables share is even higher.
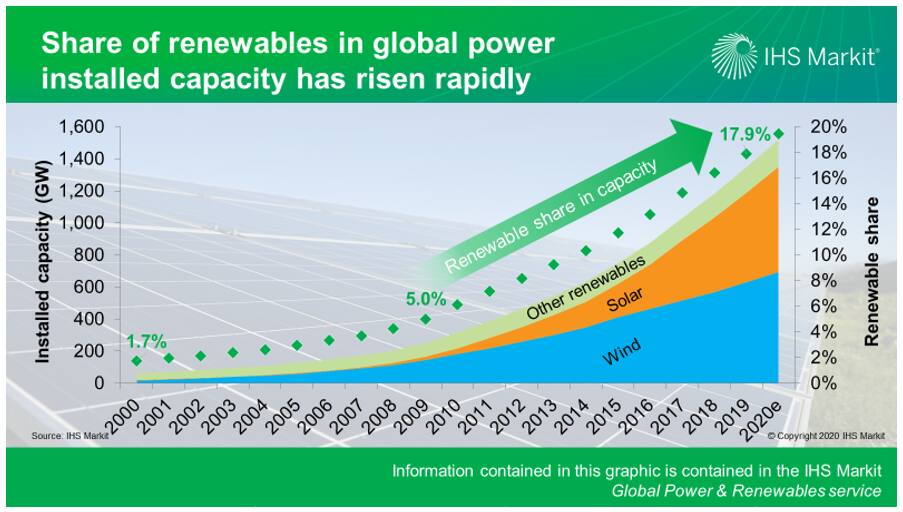
Figure 1: Share of renewables in global power installed
capacity has risen rapidly
How didrenewables and conventional power sources perform during the lockdowns?
Our power research teams based in 12 different countries compared generation data during their respective lockdown periods, to the coinciding period in 2019. Though only a few months may be compared at this stage, three themes emerged when assessing the results of five key markets in Asia, Europe, and North America:
- <span/>Coal-fired generation is down. In most markets, there was less coal-fired generation this year than last year. The year-on-year decline ranges from a 9% drop in China during January and February to a 20% drop in India in March and the first half of April.
- Solar is up. Every market analyzed showed an increase in solar PV generation in 2020 compared with the same period in 2019. For example, solar PV generation was 12% higher in Italy and 45% in PJM in the United States in March and the first half of April.
- <span/>Gas is outcompeting coal. In markets with sizeable coal and gas fleets where the two fuels compete for the residual load, gas-fired power generally emerged stronger. For example, gas plants produced 26% more power in India during March and the first half of April and 12% more power in South Korea during January and February.
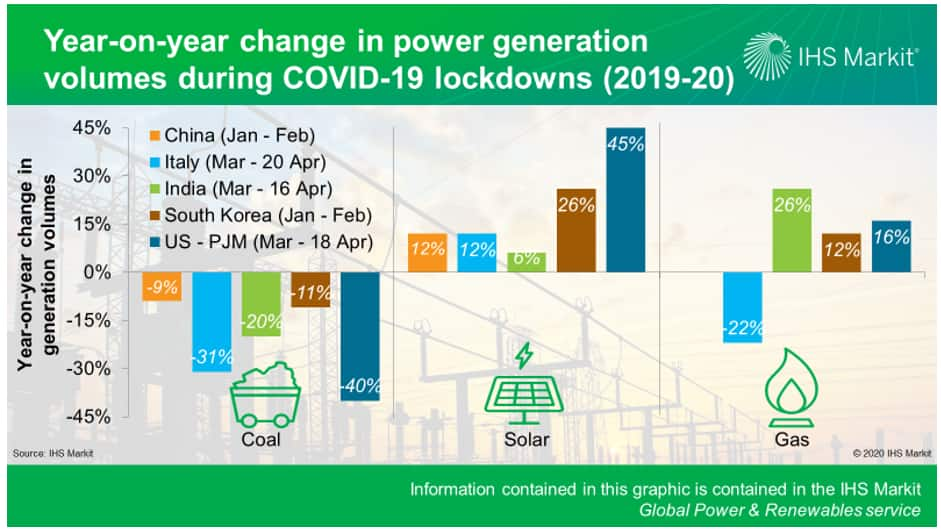
Figure 2: Year-on-year change in power generation volumes
during COVID-19 lockdowns (2019-20)
What drives the differences in power generation among the different technologies?
The local nature of power markets means that there are numerous factors - some global and some local - leading to the seemingly common outcomes across geographies. In addition to weather and its impact on demand and renewable output:
- Size matters. The growth in the installed capacity of a technology can impact how much power is produced by the technology. This is the case for solar PV in most of the markets mentioned above, as many saw double-digit growth in solar capacity over the past year.
- Competitive variable cost. In liberalized wholesale power markets, generation resources with lower variable costs get dispatched first. As renewables have near-zero variable cost, they are dispatched ahead of other technologies, while for thermal resources, the key metric determining competitiveness is fuel cost (as well as carbon price where applicable). With the global gas market in oversupply and oil prices dropping, gas prices in most markets - either freely traded or oil-indexed - have decreased significantly, making gas more competitive against coal in power generation.
- Local policies. Government restrictions and/or
incentives for different types of power generation technologies can
impact the first two drivers above. For example:
- China's renewable generation is gaining ground partly because of their non-dispatchability and preferential status in the system.
- Federal tax credits have incentivized solar PV and wind investment in the United States.
- South Korea's anti-smog policies are putting limits on coal-fired generation, which in turn boosts natural gas.
The impact described above - lower demand and lower prices in many markets - during COVID-19 will likely outlast the pandemic itself. The compilation of supply chain and permitting delays with depressed power prices in many markets, will place pressure on merchant projects, including renewables. As a result, generating technologies may have a harder time getting financed, potentially delaying new projects that had planned to come online this year and next year.
Learn more about our Global Power & Renewables research and analysis.
IHS Markit experts are available for consultation on the industries and subjects they specialize in. Meetings are virtual and can be tailored to focus on your areas of inquiry. Book in a consultation with Xizhou Zhou.
Xizhou Zhou is a Vice President and Global Managing Director of power and renewables at IHS Markit.
Posted 01 May 2020
This article was published by S&P Global Commodity Insights and not by S&P Global Ratings, which is a separately managed division of S&P Global.
{"items" : [
{"name":"share","enabled":true,"desc":"<strong>Share</strong>","mobdesc":"Share","options":[ {"name":"facebook","url":"https://www.facebook.com/sharer.php?u=http%3a%2f%2fqa.www.spglobal.com%2fcommodityinsights%2fen%2fci%2fresearch-analysis%2fcoal-gas-or-renewables-electricity-supply.html","enabled":true},{"name":"twitter","url":"https://twitter.com/intent/tweet?url=http%3a%2f%2fqa.www.spglobal.com%2fcommodityinsights%2fen%2fci%2fresearch-analysis%2fcoal-gas-or-renewables-electricity-supply.html&text=Coal%2c+gas%2c+or+renewables%3a+Electricity+supply+responding+to+lower+demand+during+COVID-19+%7c+S%26P+Global+","enabled":true},{"name":"linkedin","url":"https://www.linkedin.com/sharing/share-offsite/?url=http%3a%2f%2fqa.www.spglobal.com%2fcommodityinsights%2fen%2fci%2fresearch-analysis%2fcoal-gas-or-renewables-electricity-supply.html","enabled":true},{"name":"email","url":"?subject=Coal, gas, or renewables: Electricity supply responding to lower demand during COVID-19 | S&P Global &body=http%3a%2f%2fqa.www.spglobal.com%2fcommodityinsights%2fen%2fci%2fresearch-analysis%2fcoal-gas-or-renewables-electricity-supply.html","enabled":true},{"name":"whatsapp","url":"https://api.whatsapp.com/send?text=Coal%2c+gas%2c+or+renewables%3a+Electricity+supply+responding+to+lower+demand+during+COVID-19+%7c+S%26P+Global+ http%3a%2f%2fqa.www.spglobal.com%2fcommodityinsights%2fen%2fci%2fresearch-analysis%2fcoal-gas-or-renewables-electricity-supply.html","enabled":true}]}, {"name":"rtt","enabled":true,"mobdesc":"Top"}
]}

