Daily Global Market Summary - 12 May 2021
All major European equity indices closed higher, APAC was mixed, and US markets were sharply lower on a much higher than expected CPI release. US and benchmark European government bonds closed lower, with 10yr Bunds closing at the highest yield since May 2019. European iTraxx and CDX-NA credit indices closed wider across IG and high yield. The US dollar, oil, and natural gas closed higher, while gold, silver, and copper were lower on the day.
Please note that we are now including a link to the profiles of contributing authors who are available for one-on-one discussions through our newly launched Experts by IHS Markit platform.
Americas
- All major US equity indices closed lower for a third consecutive day; DJIA -2.0%, S&P 500 -2.1%, Nasdaq -2.7%, and Russell 2000 -3.3%.
- Energy was the only major sector in the S&P 500 that closed higher on the day.
- 10yr US govt bonds closed +8bps/1.70% yield and 30yr bonds +6bps/2.41% yield.
- CDX-NAIG closed +1bp/54bps and CDX-NAHY +7bps/301bps.
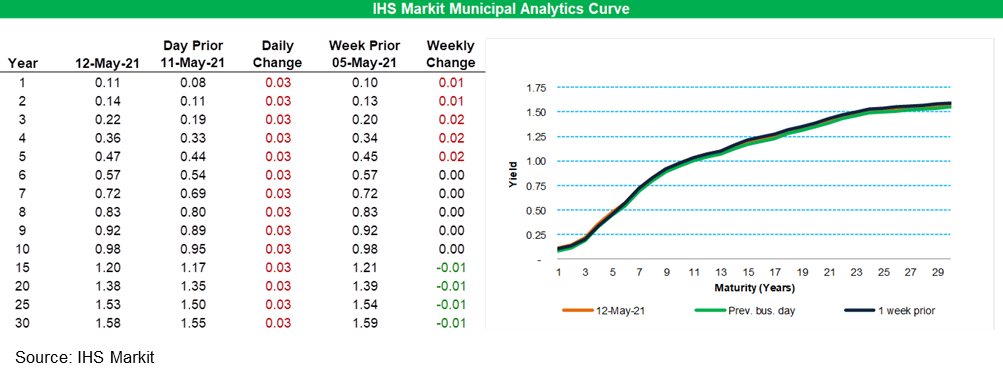
- IHS Markit's AAA Tax-Exempt Municipal Analytics Curve (MAC)
sold-off 3bps across the curve today.
- DXY US dollar index closed +0.6%/90.71. The US dollar rallied 0.4% on the CPI release, but then switched course 4 minutes later to decline 0.5% between 8:34am-9:16am ET.
- Gold closed -0.7%/$1,823 per troy oz, silver -1.5%/$27.24 per troy oz, and copper -0.5%/$4.74 per pound.
- Crude oil closed +1.2%/$66.08 per barrel and natural gas closed +0.5%/$2.97 per mmbtu.
- The US consumer price index (CPI) rose 0.8% in April, the
largest monthly increase since June 2009. This followed a 0.6%
increase in March. The core CPI, which excludes the direct effects
of movements in food and energy prices, rose 0.9%, the largest
monthly increase since April 1982. (IHS Markit Economists Ken
Matheny and Juan
Turcios)
- The rise in consumer prices in April was broad based, reflecting increased consumer demand with the reopening of the economy. Among the indices that posted substantial price increases were new vehicles (0.5%), motor vehicle insurance (2.5%), airline fares (10.2%), and used cars and trucks (10.0%). The 10.0% increase in the used cars and trucks index was the largest monthly increase in the series history and accounted for nearly a third of the rise in the all items index in April. Supply-chain issues in the new car market, primarily stemming from semiconductor shortages, are increasing demand in the used car market.
- Today's report is not just about "base-effects." Following sharp declines over March and April of last year, the core CPI had largely recovered to the previous trend by September 2020. Since September, the core CPI has advanced at a lofty 2.9% average annual rate.
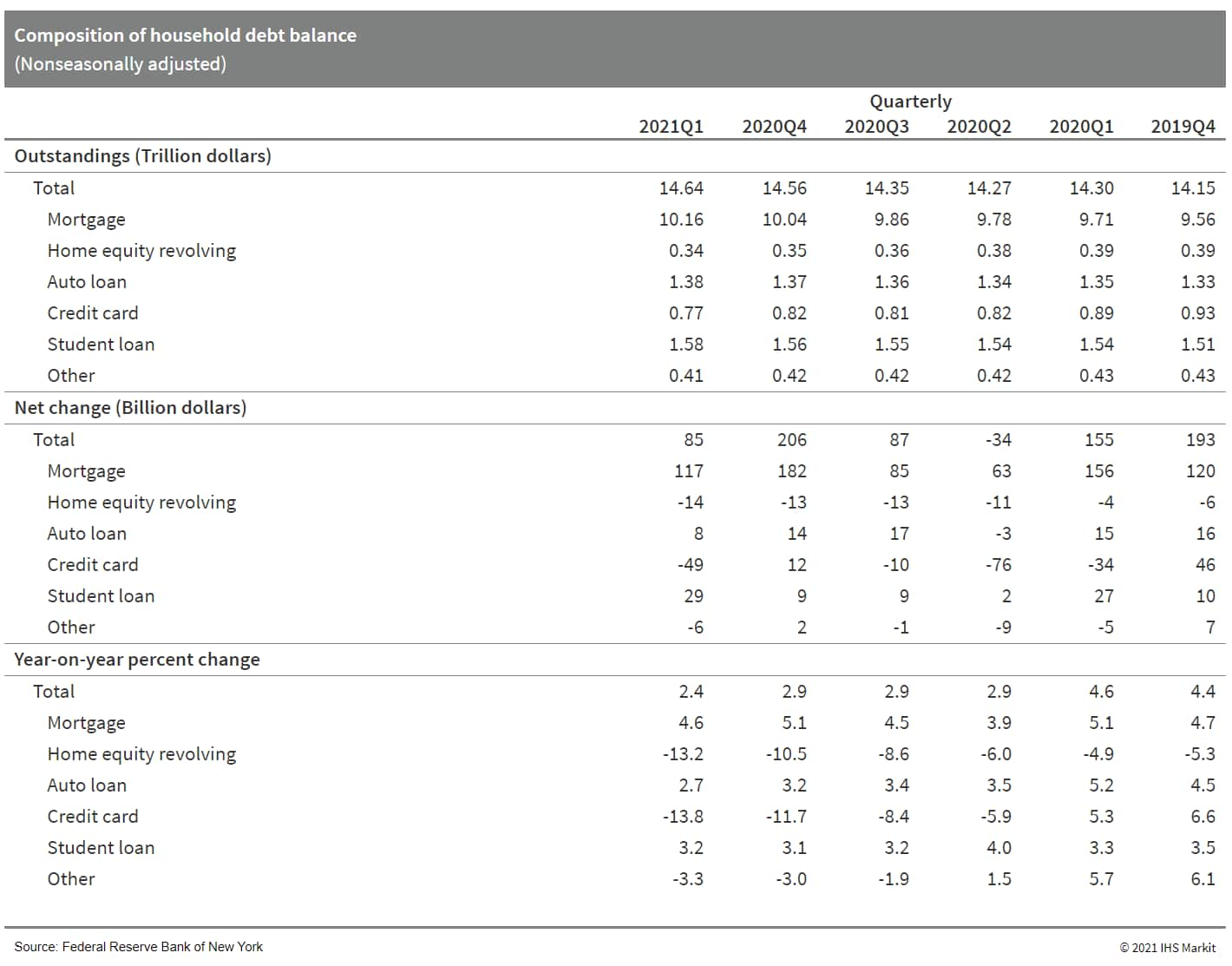
- Total US household debt rose in the first quarter by $85
billion (0.6%). The four-quarter change in total household debt
fell 0.5 percentage point to 2.4%. Outstanding household debt
totaled $14.64 trillion. (IHS Markit Economist David
Deull)
- Mortgages, the largest category of debt, were also the main source of increase in the first quarter, rising $117 billion for a four-quarter increase of 4.6% (down from 5.1% in the fourth quarter of 2020).
- Mortgage originations, which include refinances, slipped from their record high to a still extraordinary $1,138 billion. From 2010 to 2019, the quarterly average rate of mortgage originations was $447 billion.
- Nonhousing debt fell by $18 billion in the first quarter as credit card balances fell $49 billion, the fourth decrease in five quarters as stimulus payments and unemployment insurance have supplemented incomes, allowing consumers to pay down debts. Credit card debt was 13.8% below its year-earlier level, the largest four-quarter decline on record.
- Auto loans rose by $8 billion (0.6%), while student loans added $29 billion (1.9%). Four-quarter growth for these categories was 2.7% and 3.2%, respectively.
- The overall delinquency rate (the share of balances delinquent by 30 days or more) saw a sixth consecutive decline, falling by 0.1 percentage point to 3.1%, from a recent peak of 4.8% in the third quarter of 2019. These declines reflect forbearances, which insulate credit records from notations of skipped or deferred payments.
- Bankruptcy notations were added to about 114,000 consumers'
credit reports in the first quarter, a record low.
- Eli Lilly (US) has announced that it has entered into a global research collaboration with UK biotech MiNA Therapeutics to develop novel drug candidates using the latter's proprietary small activating RNA (saRNA) technology platform. Under the agreement, MiNA will utilize the platform to research up to five targets selected by Lilly that focus on the US company's priority disease areas. Lilly will be responsible for preclinical and clinical development of candidates, and will retain exclusive commercialization rights for any products resulting from the collaboration. MiNA will receive a USD25-million upfront payment and is eligible to receive potential development and commercialization milestones up to a total of USD245 million per target, as well as tiered royalties from the low-single to low-double digits on product sales resulting from the collaboration. (IHS Markit Life Sciences' Milena Izmirlieva)
- The General Motors (GM) and LG Energy Solution joint venture (JV), Ultium Cells LLC, has announced an agreement to work with Li-Cycle to recycle battery material scrap created during battery cell manufacturing. According to a joint statement from Ultium Cells and Li-Cycle, the process will allow Ultium Cells to recycle up to 100% of the material scrap including cobalt, nickel, lithium, graphite, copper, manganese and aluminum, created during battery cell manufacturing, and that 95% of the materials can then be used in production of new batteries or for adjacent industries. The partners indicate that the process for recycling the materials also emits 30% less greenhouse gas than a traditional process. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Stephanie Brinley)
- TuSimple, in partnership with Navistar, has received 6,775 reservations for a new line of trucks that are capable of Level 4 autonomous operations, according to a company statement. These trucks are purpose-built International LT Series, which are deployed with TuSimple's autonomous system and will be manufactured by Navistar beginning in 2024. Penske Truck Leasing, Schneider, and U.S. Xpress are among the first customers to place reservations for these autonomous trucks. (IHS Markit Automotive Mobility's Surabhi Rajpal)
- Chinese digital freight-matching platform Full Truck Alliance is planning an initial public offering (IPO) in New York (US) that will value the company at more than USD20 billion, reports Reuters. The company aims to raise about USD1.5 billion from its IPO and could file for listing as early as this week. Full Truck Alliance was created with the merger of Huochebang and Yunmanman in 2017 to offer an on-demand platform that connects cargo shippers with truck drivers, resembling an Uber service for trucks. The company has more than 10 million registered truck drivers and more than 5 million truck owners on its platform. (IHS Markit Automotive Mobility's Surabhi Rajpal)
Europe/Middle East/Africa
- European equity indices closed higher; UK +0.8%, Italy +0.2%, Spain +0.2%, Germany +0.2%, and France +0.2%.
- 10yr European govt bonds closed lower; Spain +2bps, France/Italy +3bps, Germany +4bps, and UK +5bps. 10yr German Bunds closed at a -0.13% yield, which is the highest close since May 2019.
- iTraxx-Europe closed +1bp/52bps and iTraxx-Xover +5bps/261bps.
- Brent crude closed +1.1%/$69.32 per barrel.
- The UK's Office for National Statistics (ONS) reports that GDP
in volume terms shrank by 1.5% quarter on quarter (q/q) in the
first quarter. This compares with upwardly revised gains of 1.3%
q/q and 16.9% q/q in the fourth and third quarters of 2020,
respectively. (IHS Markit Economist Raj
Badiani)
- In annual terms, the economy contracted by 6.1% year on year (y/y) during the first quarter, after a 9.8% drop in the full year 2020.
- In addition, GDP in the first quarter was 3.0% smaller than it was at the end of 2019, the pre-COVID-19 level.
- GDP fared better than expected during the third lockdown in
England in the first quarter for the following reasons:
- Many businesses continued to display innovation to survive the restrictions, with the ONS reporting the increasing use of "click and collect" as well as a move online.
- Supermarkets increased their product ranges to take advantage of the closure of non-essential shops.
- A notable rise in government spending on COVID-19-related medical goods and services occurred in the latter stages of 2020 and early 2021.
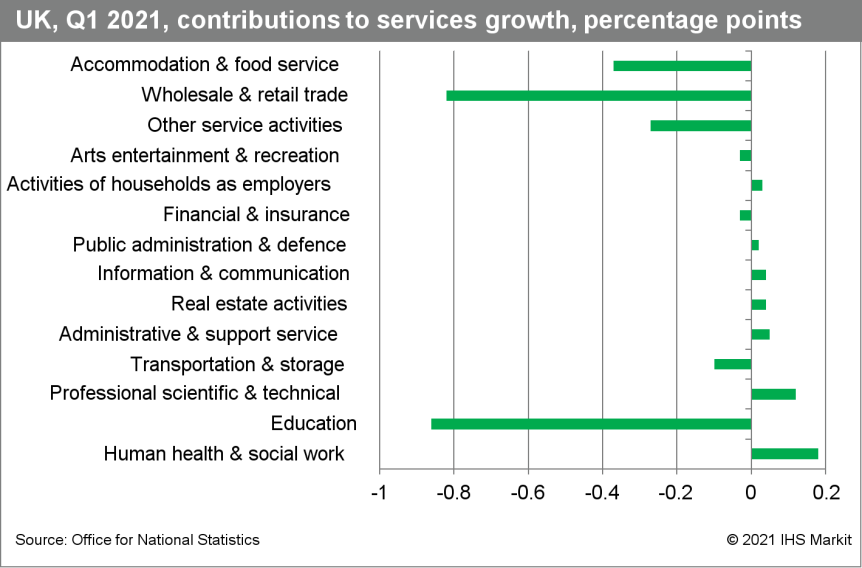
- Service-sector output shrank by 2.0% q/q in the first quarter and is 8.7% below the pre-COVID-19 level.
- The largest drag was from the education sector, with output
here falling by 11.8% q/q because of the closure of schools during
January and February as part of the government's COVID-19
restrictions
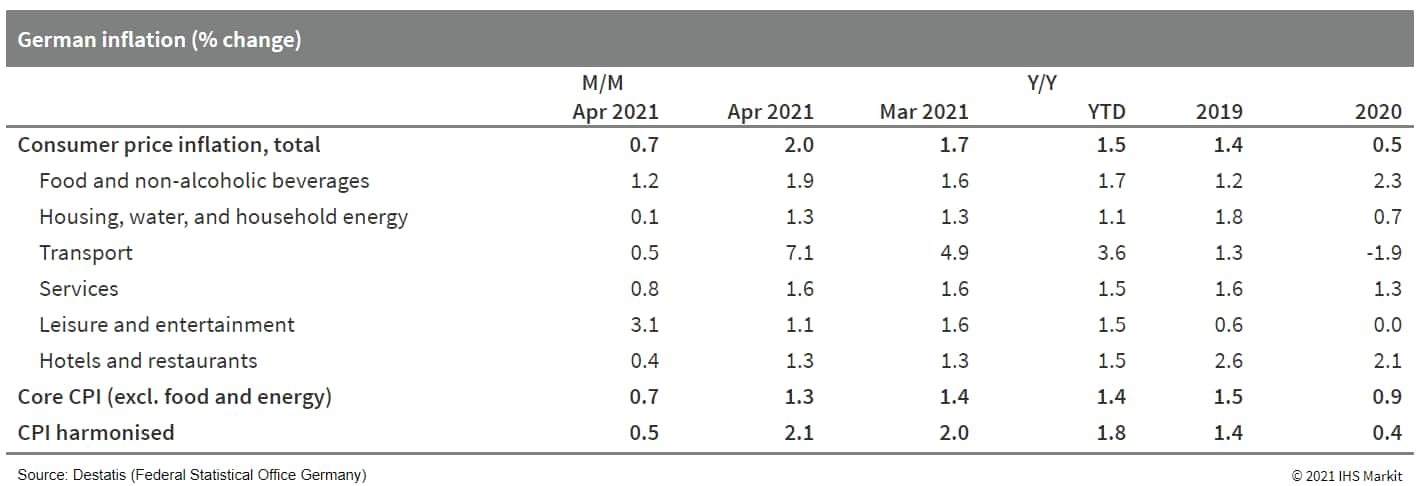
- Germany's final April inflation data based on national
methodology from the Federal Statistical Office (FSO) confirm the
"flash" data release of 29 April, showing rates of 0.7% month on
month (m/m) and 2.0% year on year (y/y), the latter increasing from
1.7% in March. This exceeds average inflation of 1.4% in 2019 and
0.5% in 2020. (IHS Markit Economist Timo
Klein)
- Mercedes-Benz Trucks has launched a collaboration with Shell to trial automatic digital fuel payments for trucks at its German stations, according to a company statement. The system has already been successfully used to make automatic digital payments using Mercedes-Benz Actros trucks fitted with a new prototype of Mercedes-Benz Trucks' previously presented digital Truck-ID. This is combined with a digital fuel card prototype that uses Shell SmartPay API technology. The Truck-ID works like an integrated ID card, so the transactions are uniquely assigned to the vehicle and automatically signed by the vehicle itself. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Tim Urquhart)
- Lanxess says its first-quarter net profits were flat year on
year (YOY) at €64.0 million ($77.6 million) on a 0.6% YOY slip in
sales, to €1.69 billion. Volumes were up 5.0% YOY with growing
demand from the automotive sector driving the increase, but lower
selling prices despite higher raw material costs, negative currency
effects, and weather-related production shutdowns in the US offset
the growth in volume, the company says. EBITDA pre exceptionals
decreased by 1.2% YOY, to €242.0 million, but beat analysts'
consensus estimate of €234.8 million provided by Vara Research
(Frankfurt, Germany). EBIT was 5.8% lower YOY, at €98 million. The
company, meanwhile, has raised its full-year forecast. (IHS Markit
Chemical Advisory)
- The company's advanced intermediates business recorded a 1.2% YOY increase in sales, to €489 million, and EBITDA pre exceptionals declined 6.1% YOY, to €77 million.
- The Lanxess specialty additives business was also hampered by the production shutdowns in the US as well as continued weak demand from the aviation industry that led to lower volumes, the company says.
- Sales of Lanxess's consumer protection business were up 3.9% YOY, to €290 million, despite lower selling prices, the company says. EBITDA pre exceptionals rose 3.0% YOY, to €69 million. The performance was driven by the continued strong agricultural chemical business of the Saltigo subsidiary and good demand for disinfectants at the material protection products segment.
- The Lanxess engineering materials business reported an 8.6% YOY increase in sales, to €377 million, boosted by increasingly strong demand from the automotive industry that drove volumes higher, the company says. EBITDA pre exceptionals was up 20.4% YOY, to €59 million, despite higher freight and energy costs, Lanxess says.
- A second estimate shows French EU-harmonised prices rising by
1.6% year on year (y/y) in April. This is slightly below a "flash"
estimate of 1.7% released in late April. (IHS Markit Economist Diego
Iscaro)
- April's inflation rate was the highest since February 2020, when it had also stood at 1.6%.
- Core inflation, which is not released with the flash figures, accelerated from 0.8% in March to 1.0% in April, a three-month high.
- Service price inflation also accelerated in April, but only slightly. Service prices went up by 1.2% y/y in April (+1.1% y/y in March), boosted by higher communication costs (+4.2% y/y) and prices of "other services" (+1.3% y/y).
- Prices of manufactured goods declined by 0.2% y/y in April, unchanged from March. The fall in prices of clothing and footwear moderated (-2.3% y/y, following a fall of 2.7% y/y in March), while prices of furniture and furnishings accelerated from +3.2% y/y to +3.6% y/y.
- Italian automotive supplier Marelli and powertrain and driveline supplier Punch have agreed to form a joint venture (JV) on 'focused e-axle solutions', according to a company statement. The companies will combine their extensive expertise in the area of electric powertrains to offer integrated systems for electric vehicles (EVs). The JV will be majority-owned by Marelli and will be focused on creating an e-axle technology for multiple OEMs, with the target markets being focused on the European and Americas. The new enterprise, Marelli Electric Powertrain Strasbourg (France) SAS, will be headquartered at Punch's site in Strasbourg, France, in proximity to major European vehicle makers. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Tim Urquhart)
- A pair of European energy companies are looking to use Norway's offshore oil production experience as a starting point for its emerging floating offshore wind sector. Norway's state-controlled Equinor and Vårgrønn, a joint venture of Italy's Eni with Norwegian equity firm HitecVision, plan to develop floating offshore wind off Utsira and Haugalandet in Norwegian waters, according to a 6 May . Norway relies on hydropower for 95% of its electricity needs, and it also had 2.2 GW of onshore wind power capacity at the end of 2019, according to IHS Markit data. It does not yet have any operational offshore wind farms. Deep, rough waters, and an uneven seabed make Norwegian waters less friendly than those of other European nations for bottom-fixed wind turbines, but the floating wind sector may grow in cost-competitiveness as the technology develops, according to a report on offshore wind commissioned by Norway's Ministry of Oil and Energy. (IHS Markit Climate and Sustainability News' Cristina Brooks)
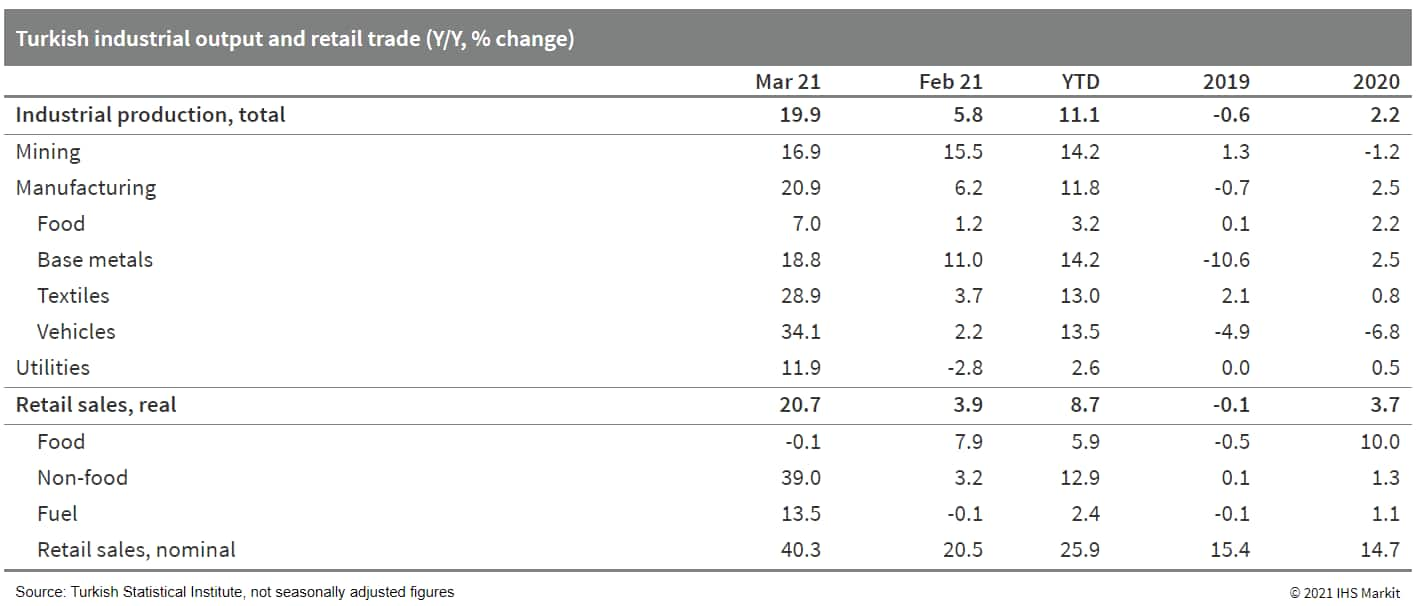
- In March, Turkish industrial production expanded by 0.7% month
on month (m/m) in seasonally and calendar adjusted data. Following
the March-April 2020 plunge in production triggered by the onset of
lockdown measures to combat the first wave of COVID-19 infections,
industrial output has steadily grown for 11 consecutive months.
Total output as of March 2021 was 9.5% higher than it had been
immediately preceding the pandemic. (IHS Markit Economist Andrew
Birch)
- Steady industrial gains - buoyed by the resilient European production cycle driving export demand - have returned employment levels to above pre-pandemic levels as well. There was a particularly sharp year-on-year (y/y) surge in employment in March due to the base effects caused by the onset of the pandemic in March 2020.
- Greater employment and sustained, strong credit growth have
continued to fuel increased retail trade. In March, the total
volume of retail trade increased by 5.1% m/m in seasonally and
calendar adjusted data. Total retail trade expanded m/m in each of
the first three months of 2021 despite increasing lockdown measures
implemented in the face of renewed COVID-19 infections.
- Turkey posted a current-account deficit of USD7.8 billion in
the first quarter of 2021, down by USD1.1 billion year on year
(y/y), but still large as a share of GDP. Vigorous merchandise
export growth reduced the trade gap, which was responsible for the
narrowing of the headline current-account imbalance. (IHS Markit
Economist Andrew
Birch)
- On the other hand, the failure of tourism or other service exports to recover from COVID-19 in the first quarter - total service exports dropped by nearly 19% y/y - led to a sharp narrowing of the services balances. This worsening offset much of the positive impact of the smaller merchandise-trade deficit on the headline current-account balance.
- Turkey also recorded a massive, record-setting net outflow of portfolio investment in March 2020, totaling USD5.7 billion. Given the sharp plunge in the lira during March following the replacement of the central bank governor, the report of the strong net portfolio investment was not a surprise. The sheer size of the lost investment, however, reflects the deep market distrust of the new leadership.
Asia-Pacific
- APAC equity markets closed mixed; Hong Kong +0.8%, Mainland China +0.6%, Australia -0.7%, India -1.0%, South Korea -1.5%, and Japan -1.6%.
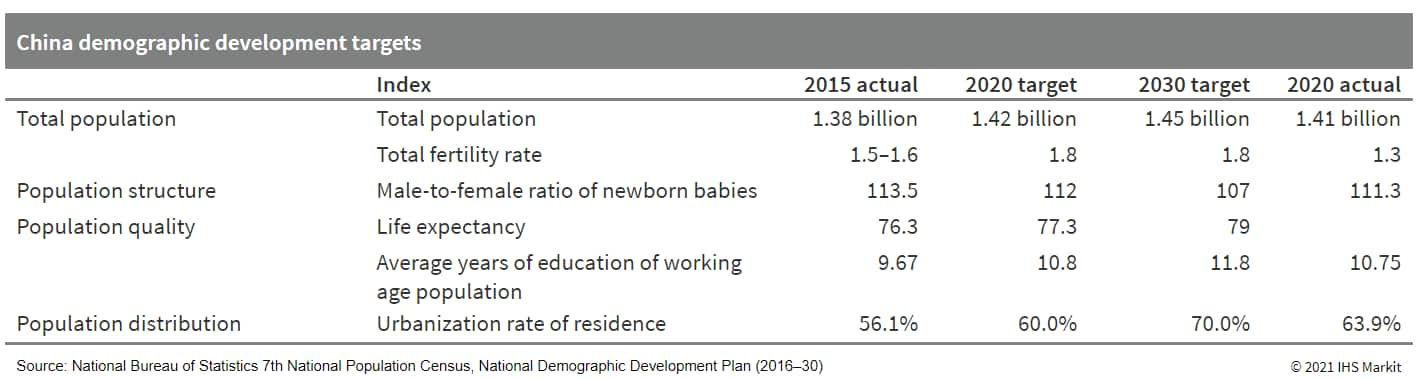
- China's population topped 1.41 billion at the end of 2020,
increasing by 5.38% from 2010, according to the 7th National
Population Census report released by the National Bureau of
Statistics (NBS) on 11 May. The annual average growth rate for the
past decade, at 0.53%, is lower than the 0.57% average annual
growth rate for the 2000-10 decade. (IHS Markit Economist Yating
Xu)
- China's elderly population continues to grow, with the percentage of people aged above 65 increasing by 4.6 points to 13.5% during 2010-20. Moreover, there are significant differences in the level of aging between rural and urban areas, with the proportion of people aged over 65 in rural areas standing at 17.7%, significantly higher than the national level.
- The percentage of children aged below 14 years only increased 1.35 points, and the share of the working-age population (comprising those aged between 15 and 59) fell by 6.8 points. The average age of China's population is 38.8 years, which is higher than the United States' average population age of 38 years.
- The birth rate in China declined to a low level, registering 1.2 million newborn babies in 2020, representing a 18% decline from the 2019 level. This reflects the significant decline in China's total fertility rate and decrease in the number of women of child-bearing age. The NBS attributed the drop in the number of child-bearing-aged women to the impact of the COVID-19 crisis, which increased concerns over giving birth, and the fading effects of the two-child policy, which was first rolled out in 2016.
- The total fertility rate declined to 1.3, far below the
expected rate of 1.8 laid out in the National Demographic
Development Plan (2016-30), and also lower than Japan's 2019
fertility rate of 1.38.
- According to media reports, Tesla has reconsidered plans to purchase more land near its Shanghai plant, being considered for increasing capacity. Reuters, citing unnamed sources, says that Tesla has halted plans to buy land across from the current plant, on an eventual plan to use China as an export base. Reuters reports that Tesla refrained from bidding on a specific land parcel in March 2021 as it no longer plans to boost China output significantly. Reportedly, the reason for the change of heart is concerns over US-China trade, as exports to the US were considered. The US has not pulled back its tariff of 25% on vehicles imported from China. Reuters also quotes a Tesla spokesperson as saying that Shanghai is progressing "as planned," and not commenting on the potential for buying new land. The report also has land with the current plant currently being used for parking, which could be used to expand capacity. Reuters reports that the Shanghai facility has capacity for 500,000 units per year, a figure Tesla reported with its first-quarter 2021 financial reporting as well, but that the company is building at a 450,000-unit pace today. The company is, however, reportedly building facilities in Shanghai for repairing and reproducing electric motors and battery cells, as well as planning to build electric vehicle (EV) chargers at the plant. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Stephanie Brinley)
- Autonomous vehicle (AV) startup Pony.ai's smart logistics subsidiary has received a freight road transport business permit from the local authority of China's Nansha district, in Guangzhou. Following this, the subsidiary will begin commercial operations of transporting cargo by deploying autonomous trucks in the district, reports Gasgoo. (IHS Markit Automotive Mobility's Surabhi Rajpal)
- The Japan Automobile Importers Association (JAIA) has reported
that imported vehicle sales in the country increased by 54.5% year
on year (y/y) to 22,082 units in April. (IHS Markit
AutoIntelligence's Isha Sharma)
- This figure includes sales of foreign brands' imported vehicles, which increased 47.8% y/y to 16,501 units last month, and domestic brands' imported vehicles, which increased by 78.5% y/y to 5,581 units.
- By brand, Mercedes-Benz led the imported market with a 14.55% share during April, its sales coming in at 3,213 units, compared with 2,288 units in April 2020. It was followed by Nissan with sales of 2,292 units, equating to a market share of 10.38%; and BMW with 2,263 units, accounting for a market share of 10.25%.
- In the year to date (YTD), imported vehicle sales are up 26.4% y/y at 123,446 units.
- At the US-organized climate summit in April, Japan made one of the most substantial new GHG emissions reduction commitments, raising its target to a 46% cut from a 2013 baseline—a goal that seems aggressive, but achievable, based on the country's track record over the last six years. Japan's prior commitment was for a reduction of 26% from 2013 levels, backed by a net-zero commitment for 2050. Japan's total GHG emissions in FY 2019 were 1,212 million mt CO2e, a reduction of 2.9% from FY 2018, according to its annual emissions inventory published in April. This represents a reduction in emissions of 15% since FY 2013, according to information submitted to the United Nations on 31 March as an update to Japan's nationally determined contribution. Previously, its goal for 2030 was 1,042 million mt CO2-equivalent, but the new target will be about 761 million mt CO2e. "Their target before, relatively speaking, wasn't incredibly ambitious," said Anna Mosby, IHS Markit principal research analyst. "The new target is significantly more ambitious. They can meet this new target if they maintain that pace," she said. (IHS Markit Climate and Sustainability News' Kevin Adler)
- With stronger-than-expected tax revenues bolstered by higher
commodity prices and a quickly recovering domestic labor market,
Australia's projected deficit for FY 2021-22 is down slightly from
the Mid-Year Economic and Fiscal Outlook (MYEFO) in December 2020,
which projected a shortfall of 5.3% of GDP for the underlying cash
balance. (IHS Markit Economists Hannah Cotillon and Bree
Neff)
- According to the Australian Treasury, for FY 2021-22 receipts (primarily tax receipts) will be up by AUD23.6 billion (USD18.5 billion) versus the MYEFO estimate, although they are still anticipated to fall by a modest 3.5% for the year. The fiscal shortfall for the current fiscal year has also been revised down to 7.8% of GDP from 9.9% in the MYEFO, also due to the stronger tax receipts.
- Expenditures in nominal terms are planned to fall 10.9% in FY 2021-22, after surging 20.2% in FY 2020-21, owing to the unwinding of sizeable programs such as the JobKeeper wage subsidy, and JobSeeker Coronavirus supplement payments. That said, the December MYEFO projections called for a reduction in expenditures of closer to 15.5% for FY 2021-22, indicating that the government's fiscal consolidation timelines are being pushed out, although there is also support from a stronger revenue forecast.
- The government projects fiscal shortfalls to persist for the next decade, with the underlying cash balance reaching a projected deficit worth 1.3% of GDP in FY 2031-32. The government projects gross public debt to stabilize around 51% of GDP in the latter part of this decade.
- From the sovereign risk perspective, IHS Markit does not have any strong concerns about the forward projections for Australian public debt and fiscal deficits. This is because the forward projections keep central (Commonwealth) government debt around the 50% of GDP mark, and we do not generally consider this to be risky from a solvency standpoint.
S&P Global provides industry-leading data, software and technology platforms and managed services to tackle some of the most difficult challenges in financial markets. We help our customers better understand complicated markets, reduce risk, operate more efficiently and comply with financial regulation.
This article was published by S&P Global Market Intelligence and not by S&P Global Ratings, which is a separately managed division of S&P Global.
