Daily Global Market Summary - 17 June 2021
US, European, and APAC equity markets closed mixed. US government bonds closed sharply higher and European government bonds closed lower. European iTraxx and CDX-NA credit indices were close to flat on the day across IG and high yield. The US dollar and natural gas closed higher, while oil, gold, silver, and copper closed sharply lower.
Please note that we are now including a link to the profiles of contributing authors who are available for one-on-one discussions through our newly launched Experts by IHS Markit platform.
Americas
- Major US equity indices closed mixed; Nasdaq +0.9%, S&P 500 flat, DJIA -0.8%, and Russell 2000 -1.2%.
- 10yr US govt bonds closed -7bps/1.51% yield and -12bps/2.10% yield, with yields dropping as low as 1.44% and 2.05%, respectively, at 1:00pm ET.
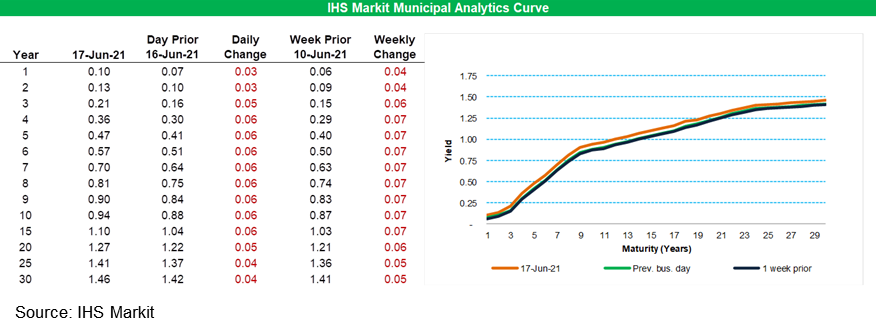
- IHS Markit's AAA Tax-Exempt Municipal Analytics Curve (MAC)
sold-off 6bps across 4-15 year maturities and 3-5bps across the
other maturities.
- CDX-NAIG closed +1bp/50bps and CDX-NAHY flat/281bps.
- DXY US dollar index closed +0.8%/91.89, which is +2.5% since 24 May.
- Gold closed -4.7%/$1,775 per troy oz, silver -7.0%/$25.86 per troy oz, and copper -4.7%/$4.18 per pound.
- Crude oil closed -1.5%/$71.04 per barrel and natural gas closed +0.1%/$3.25 per mmbtu.
- US seasonally adjusted (SA) initial claims for unemployment
insurance rose by 37,000 to 412,000 in the week ended 12 June,
rising for the first time since 24 April. Pennsylvania (up 21,600),
California (up 15,700), and Kentucky (up 9,100) were the largest
contributors to the increase in claims in the week ended 12 June.
(IHS Markit Economist Akshat Goel)
- Seasonally adjusted continuing claims (in regular state programs) edged up by 1,000 to 3,518,000 in the week ended 5 June. The insured unemployment rate was unchanged at 2.5%.
- In the week ended 29 May, continuing claims for Pandemic Emergency Unemployment Compensation (PEUC) fell by 74,507 to 5,157,445.
- There were 118,025 unadjusted initial claims for Pandemic Unemployment Assistance (PUA) in the week ended 12 June. In the week ended 29 May, continuing claims for PUA dropped by 253,918 to 6,120,596.
- In the week ended 29 May, the unadjusted total of continuing claims for benefits in all programs fell by 559,873 to 14,828,950.
- Governors in many states—25 at last count—have announced an early end to pandemic-related federal unemployment programs. The federal pandemic-related unemployment programs, which include extra $300-a-week payments, the PUA, and the PEUC, were set to expire on 6 September. They are now slated to expire between 12 June and 19 July in the 25 states that have opted out.
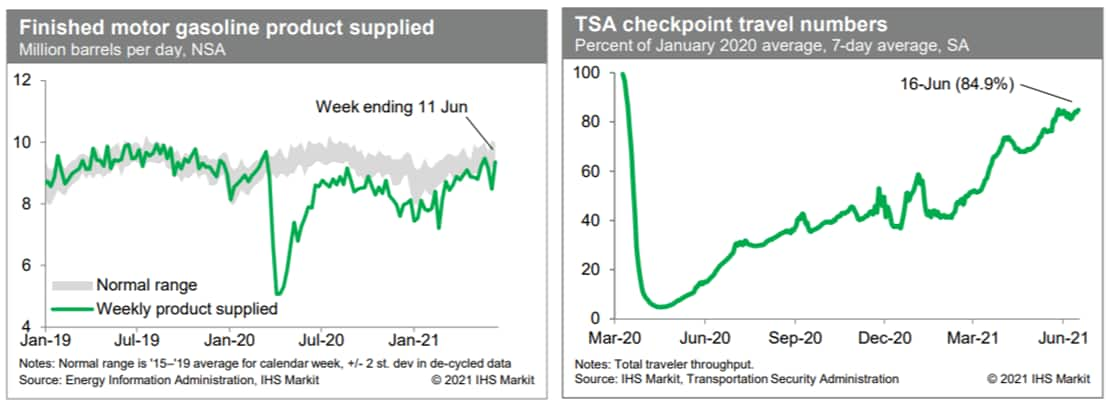
- US consumption of gasoline rebounded last week and was within a
range that we would consider normal for this time of year. This
series has been volatile in recent weeks, but the trend continues
to indicate nearly full recovery in internal mobility. Meanwhile,
passenger throughput at US airports (after seasonal adjustment) has
been running at about 85% of the January 2020 pace in recent days,
close to readings over the last couple of weeks. The recovery in
air travel seems to have stalled for the time being. (IHS Markit
Economists Ben
Herzon and Joel
Prakken)
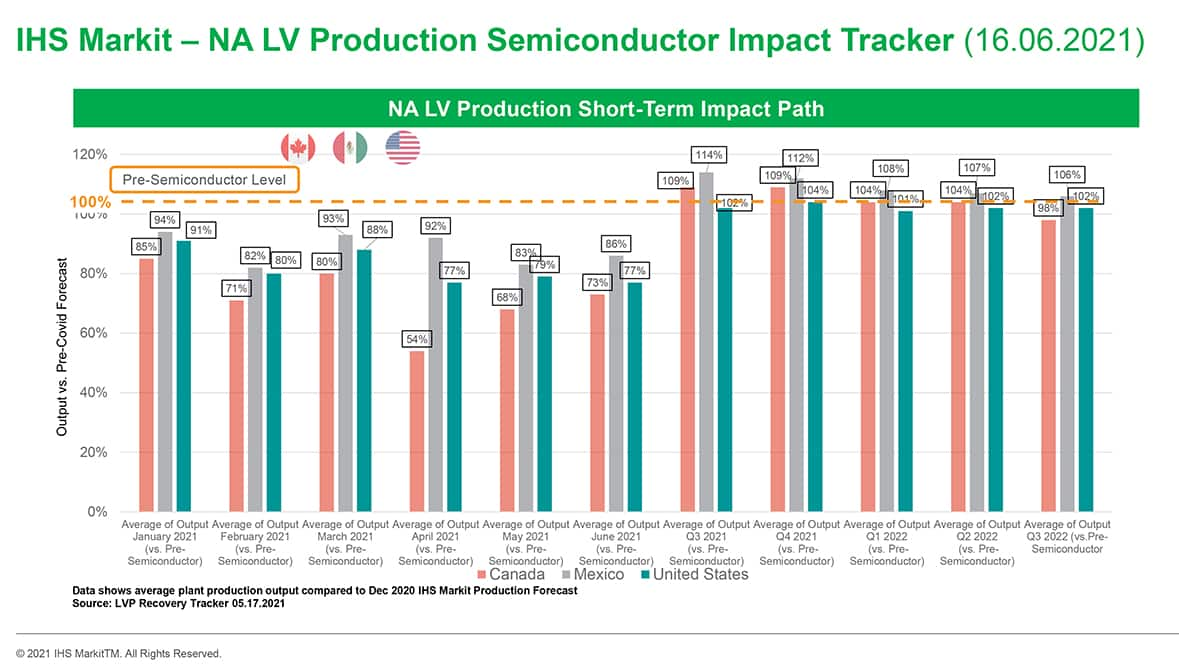
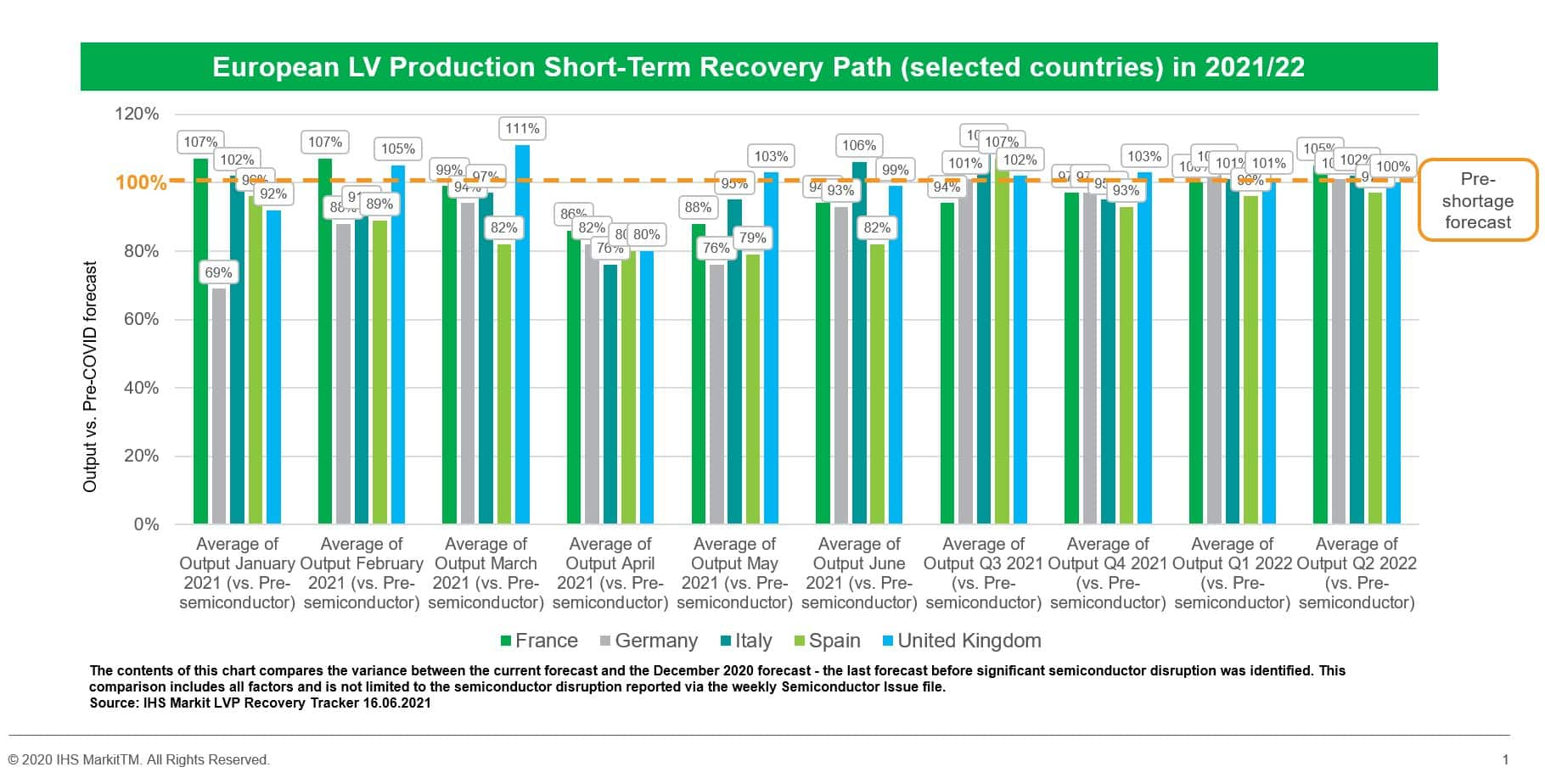
- Although there have been no repeats of regional industry-wide
production shutdowns as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic since the
second quarter of 2020, supply-chain issues have come to the
forefront. The most urgent and pervasive of these issues is a
shortage of semiconductors used in electronic control units. This
report provides a current snapshot of the impact of this issue on
light-vehicle production in North and South America. Light-vehicle
manufacturers suffered increased disruption to the supply of
systems using semiconductors in the first quarter of 2021. The
industry is as exposed to the issue in the second quarter as it was
in the first. Stabilization of microchip supplies may not emerge
until the fourth quarter of 2021 and lost production recovery
efforts only start in early 2022. This pattern will further distort
production seasonality and have a significant effect on the overall
level of output in 2021. This report provides an overview of IHS
Markit's current expectations for the production loss and recovery
from this issue. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Stephanie
Brinley)
- GM has announced an increase in planned electric vehicle (EV) and autonomous vehicle investment to USD35 billion through 2025, including funding for two new US battery plants, EVs for commercial fleet buyers, and its third-generation fuel cell by mid-decade. GM did not provide details of any specific funding allocation. This increased funding means GM's announced investment is higher than the investment planned by Ford; Ford has committed to spending USD30 billion through 2025. GM continues to increase its investment in EVs, supported by positive market response to date, as well as the policy landscape. GM's announcement of new battery plants in the US comes against the backdrop of President Joe Biden's administration proposing significant government spending on EV infrastructure and potentially revising government incentives. Those revisions to available incentives may involve preferences for US EV and battery production. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Stephanie Brinley)
- Electric vehicle (EV) manufacturer Polestar has announced that its third product, an upcoming utility vehicle, is to be produced at sister brand Volvo Cars' plant in South Carolina, United States. In a company statement, Dennis Nobelius, chief operating officer at Polestar, said, "Production in the USA reduces delivery times as well as the environmental impact associated with shipping vehicles around the world. It will even have a positive impact on the price of Polestar 3. All of this makes the brand even more competitive in the critical American sales market." Polestar says the Polestar 3 will introduce a new generation of EV architecture, which it says was "designed from scratch for full electrification". (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Stephanie Brinley)
- Autonomous truck startup TuSimple will open a new facility in Texas (US), reports Automotive News. This will expand the company's autonomous operations eastward to serve the "Texas Triangle," an area that includes Dallas, Houston, San Antonio, and Austin. The facility will enable TuSimple to add 3,000 miles to its network and put trucks to work hauling freight on the roads of southeastern US states within six months. (IHS Markit Automotive Mobility's Surabhi Rajpal)
- Alphabet Inc's autonomous vehicle (AV) unit Waymo has raised USD2.5 billion in a recent funding round, according to a company statement. Investors in the latest round include Alphabet, Andreessen Horowitz, the Canada Pension Plan Investment Board, Fidelity Management & Research Co. and Tiger Global, among others. The company plans to use the proceeds to continue advancing its AV platform, Waymo Driver, as well as growing its team. (IHS Markit Automotive Mobility's Surabhi Rajpal)
- Coconut water company Vita Coco may go public this year. Its owner, All Market Inc, is planning an IPO for later this year, according to Bloomberg, Reuters and other sources. All Market also owns Runa energy drinks, which it acquired in 2018, and the Ever & Ever water brand, and Vita Coco's listing could be worth as much as USD2.0 billion. Launched in New York in 2004, Vita Coco now makes flavored, carbonated and caffeinated coconut waters, as well as coconut oil and milk alternatives. PepsiCo entered into talks to buy All Market in 2017, which would have given it the brand, but the then price of around USD1.0 billion was reportedly too high for the soft drinks giant. In 2014, All Market sold a 25% stake in Vita Coco to Red Bull China, which gave it entry to that country. (IHS Markit Food and Agricultural Commodities' Neil Murray)
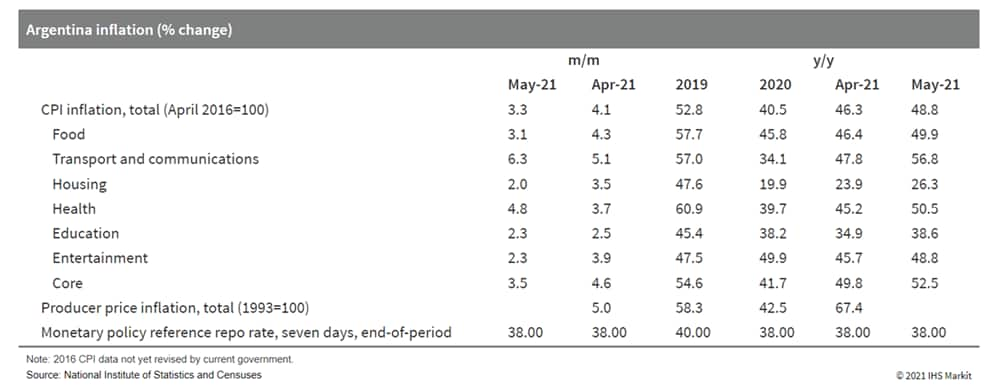
- Argentina's inflation rate in May was driven by price increases
in the food and beverages category, with substantial price rises
for white rice, beef and other meats, bread, dairy products, and
fresh produce, as well as increases in the transportation, health,
and alcoholic beverages sectors. The rise in the transportation
component was mainly driven by the increase in gasoline (petrol)
prices, vehicle prices, and the cost of personal vehicle
maintenance. (IHS Markit Economist Paula
Diosquez-Rice)
- The prices of regulated items increased by 3.8% m/m, driven by the adjustment in gasoline prices, while the prices of seasonal items rose by 1.5% m/m. The core inflation rate stood at 3.5% m/m. Wholesale prices climbed by 67% year on year (y/y) in April, a significant acceleration compared with the previous month. The annual CPI rate in May continued the accelerating trend of the past few months.
- Inflation expectations for the next 12 months rose in May;
Torcuato Di Tella University reported a median of 50% y/y, similar
to the previous month. However, the average expected annual
inflation rate rose to 50.2%. The inflation expectation survey by
the country's central bank, the Central Bank of the Argentine
Republic (Banco Central de la República Argentina: BCRA), shows a
median of 43.3% in May.
Europe/Middle East/Africa
- Major European equity indices closed mixed; France +0.2%, Germany +0.1%, Spain -0.1%, Italy -0.2%, and UK -0.4%.
- 10yr European govt bonds closed lower; Italy +5bps, UK +4bps, Spain +3bps, France +2bps, and Germany +1bp.
- iTraxx-Europe closed flat/47bps and iTraxx-Xover flat/234bps.
- Brent crude closed -1.8%/$73.08 per barrel.
- The latest run of "hard" activity data for the eurozone, in the
form of April's retail sales, industrial production, trade, and
construction output data, offer rather mixed signals for near-term
growth prospects. Still, in tandem with the resurgence in leading
indicators over recent months, including IHS Markit's PMIs, we
continue to expect a marked acceleration in growth momentum from
late in the second quarter as containment measures are eased. (IHS
Markit Economist Ken
Wattret)
- Starting with the positive news, eurozone industrial production rose by 0.8% month on month (m/m) in April, the 11th increase in 12 months. This leaves production only marginally below (-0.3%) its pre-pandemic level back in February 2020.
- April's gains were broad-based across good types, with production of consumer durable goods particularly robust (+3.4% m/m). Relative to pre-pandemic levels, production of intermediate goods (+2.2%) and consumer durable goods (1.9%) outperformed.
- Eurozone construction output, meanwhile, dropped by 2.2% m/m in April, albeit following a 4.1% m/m surge in March. Following the decline, construction output is now 2.3% below its February 2020 level, although an array of survey data remain indicative of very favorable conditions in the sector. The European Commission's April sentiment index, for example, was 17 points above its long-run average.
- Exports (in value terms) fell by 2.3% m/m, the biggest decline since April 2020. Although March's data now show a revised 2.8% m/m increase, compared with an initial small decline, the three-month on three-month rate of increase in exports slowed to 1.9% in April nonetheless. This was the lowest growth rate since the post-COVID-19 recovery started a year previously.
- As of April, exports were 3.9% below their pre-pandemic level in February 2020, with imports, in contrast, 5.7% above where they were before COVID-19 struck.
- With imports rising by 2.4% m/m in April, the third strong increase in succession, the eurozone's monthly trade surplus plunged to EUR9.4 billion (USD11.2 billion), the lowest level since May 2020. This is roughly one-third of the average trade surplus over the first two months of 2021.
- While the situation regarding the COVID-19 pandemic is being
brought under control and vaccination programs are being rolled out
across Europe, the issue of automotive semiconductor shortages is
also hurting European production and is likely to continue to do so
for some time. Although the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic across
Europe is much diminished, IHS Markit is providing a measured and
analytical view of the vehicle production landscape as the
situation unfolds, with a renewed focus on the impact of
semiconductor supply shortages. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Tim
Urquhart)
- BMW is to begin final road trials of its latest fuel vehicle ahead of small volume series production, according to a company statement. The near-production-ready prototypes will be trialed across Europe ahead of the plan to offer the X5-based model to customers in limited numbers from late 2022. BMW says it is still looking at fuel cell technology, 'especially for customers who do not have their own access to electric charging infrastructure or who frequently drive long distances'. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Tim Urquhart)
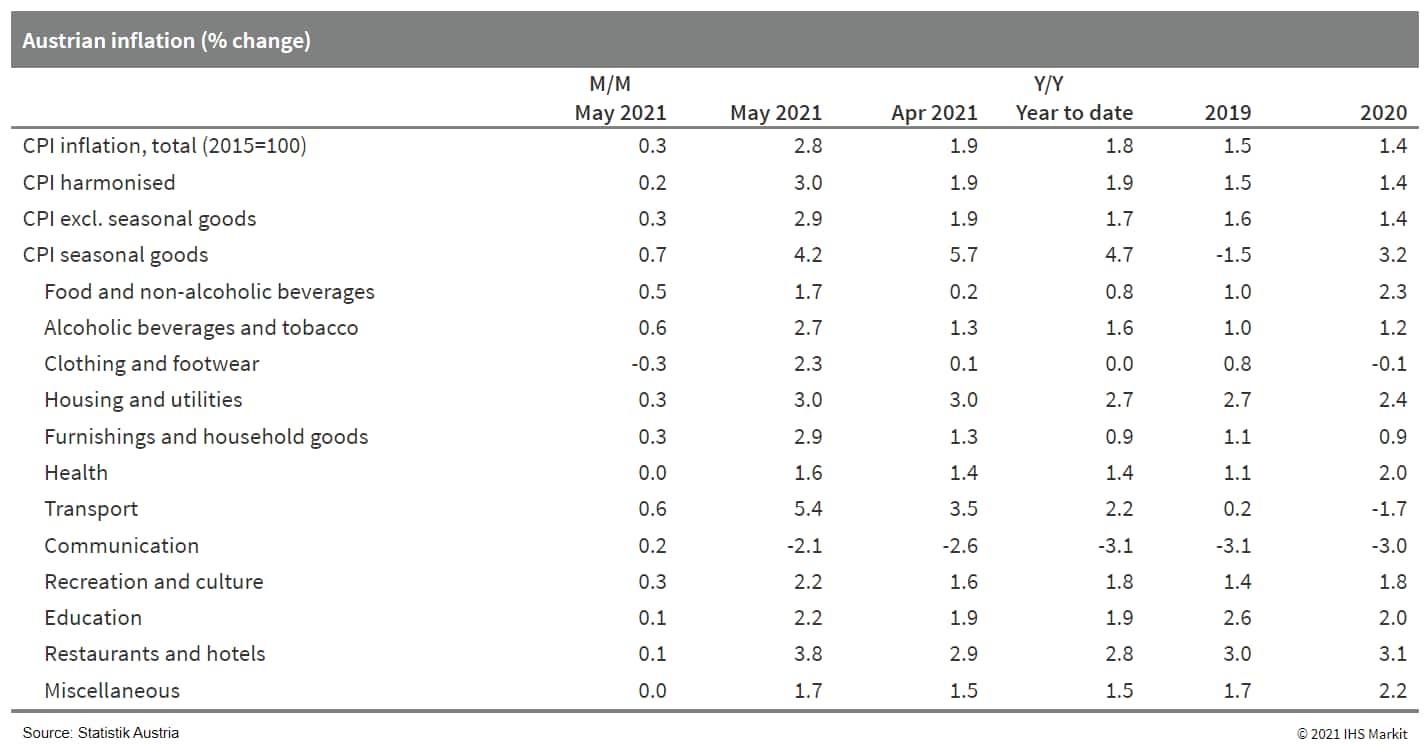
- Statistics Austria data reveal a 0.3% month-on-month (m/m)
increase in the consumer price index (CPI) in May, which exceeds
the long-term average for this month by roughly 0.2 percentage
point. (IHS Markit Economist Timo
Klein)
- Owing to additional major base effects linked to the oil price plunge a year earlier, headline inflation according to the national measure jumped from April's 1.9% to 2.8% year on year (y/y).
- The EU-harmonized measure, which has a different weighting pattern (higher weights for fuel and restaurants and hotels and lower weights for insurance services and housing maintenance), increased by only 0.2% m/m in May.
- Even larger base effects boosted its annual rate from April's
1.9% to 3.0% y/y. The gap with the eurozone average (2.0% in May)
thus rebounded from 0.3 to 1.0 percentage point, which clearly
exceeds the 0.7-percentage-point long-term average observed during
2011-20.
- The Swiss National Bank (SNB) has kept its key policy and
deposit rates at -0.75% at its regular quarterly review and
stressed that it will continue to provide the banking system with
"adequate" (changed from "ample") liquidity. As at the last three
reviews, it calls the Swiss franc "highly valued", while refraining
from using the term "overvalued". It repeats that it is prepared to
intervene in the currency market, emphasizing that its monetary
policy is instrumental in leaning against the franc's general
appreciation tendency. The SNB bought foreign currencies to the
tune of CHF110 billion (USD120 billion) in 2020, up sharply from
just CHF13 billion in 2019, but intervention activity has declined
markedly in 2021 so far. (IHS Markit Economist Timo
Klein)
- The June report highlights a near-term increase in the SNB's inflation projections. Pointing to higher prices for oil, tourism-related services, and goods affected by global supply-chain disruption, the SNB estimates - based as always on the technical assumption of steady policy at the latest level (i.e. -0.75%) - that inflation will be 0.4% in 2021 (revised up from 0.2% projected in March), 0.6% in 2022 (revised up from 0.4%), and also 0.6% in 2023 (revised up from 0.5%). With respect to the quarterly pattern, the projection for the fourth quarter of 2021 was revised up the most, from 0.6% to 1.0%, although a similar adjustment had been made at the March review already.
- The quarterly forecast for the end of the SNB's three-year forecasting horizon in the first quarter of 2024 is 0.8%, only modestly higher than the previous review's end-of-horizon projection of 0.6%. The SNB stresses that its long-term inflation forecast is essentially unchanged, adding that survey data signal that inflation expectations remain moored at around 1%, well below the central bank's critical level of 2.0%.
- Volvo Cars has announced that it is in discussions with Swedish steel-maker SSAB to become the first light-vehicle manufacturer to use steel that has reduced carbon emissions in its manufacture. According to a statement, the automaker plans to work with SSAB on its HYBRIT initiative, which is in conjunction with iron-ore producer LKAB and energy firm Vattenfall. Initially, the steel that will be sourced from a pilot plant in Luleå (Sweden). Volvo Cars added that the steel will be "used for testing purposes and may be used in a concept car". (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Ian Fletcher)
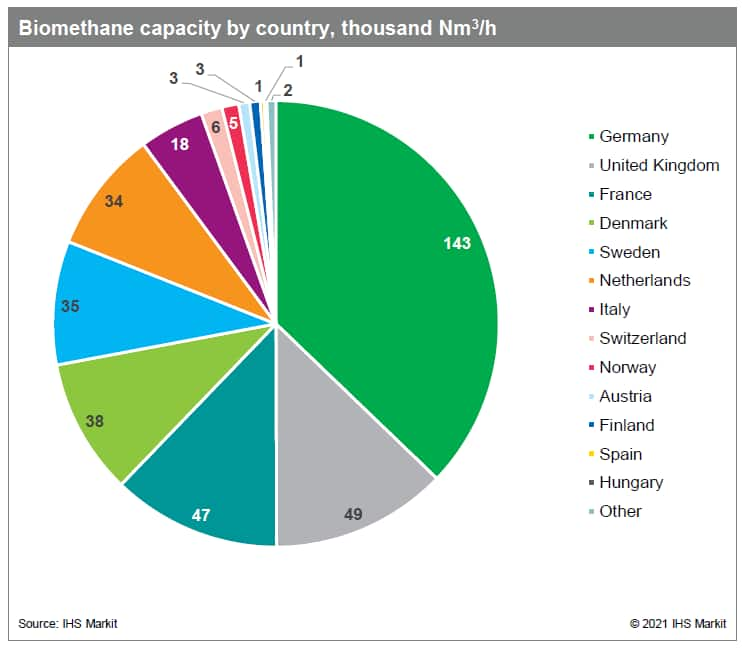
- Central and eastern Europe's path to decarbonization is set to
get a boost from biomethane, with regional production capacity
poised to surge as the current decade progresses, according to a
senior executive at German energy company Uniper. Biomethane could
replace conventional natural gas in the electricity generation,
industrial, fuel, and heating sectors, in addition to providing a
cleaner source of fuel for power stations than coal, which
currently dominates electricity production in countries such as
Poland. Biomethane is a source of methane produced either by
"upgrading" biogas or through the gasification of solid biomass.
Poland, Hungary, and Romania have a combined biomethane production
capacity potential of up to 100 TWh, Peter Arp, Uniper vice
president, origination CEE, said during an Atlantic Council
conference on central and eastern Europe 10 June. Of that, 50% is
located in Poland, less than 20% in Romania, and the rest in
Hungary, he told Net-Zero Business Daily in a phone interview 15
June. In contrast, Germany (see graphic below; for reference 11 TWh
equals about 1 billion cubic meters), Europe's largest biomethane
market at the moment, currently has around 10 TWh of capacity, he
said in the interview. (IHS Markit Climate and Sustainability News'
Keiron Greenhalgh)
- Temsa, a Turkish automotive joint venture (JV) between Sabanci Holding and PPF Group, along with Aselsan, a Turkish defence company, have launched the Avenue electric bus, reports Daily Sabah. According to the source, the electric vehicle (EV) is completely locally manufactured and is ready for mass production. The vehicle will be equipped with Aselsan's electric traction systems, electric motor, traction inverter, main computer and instrument panel, and has a range of 80 km on a single full charge, which takes about 15 minutes. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Tarun Thakur)
Asia-Pacific
- APAC equity markets closed mixed; Hong Kong +0.4%, Mainland China +0.2%, India -0.3%, Australia -0.4%, South Korea -0.4%, and Japan -0.9%.
- Mainland China's year-on-year (y/y) real industrial value-added
growth continued to fall from 9.8% in April to 8.8% in May as a
result of a rising baseline. Meanwhile, the growth rate on a
two-year (2020-21) average basis declined by 0.2 percentage point
to 6.6% following a temporary uptick in April. The month-on-month
growth figure remained at 0.5%, unchanged from the previous month.
(IHS Markit Economist Yating
Xu)
- By sector, high-tech manufacturing value-added growth continued to outpace the headline growth, which grew 13.1% (on 2020-21 average basis), up 5.5 percentage points from April.
- Driven by the acceleration in demand for vaccines, pharmaceutical manufacturing growth expanded by 34.0% y/y in May, up 15 percentage points from April. By product, the contraction in automobile production due to the semiconductor shortage remained the dominant contributor to the headline moderation. The production of steel and cement also declined, owing in part to the drop in infrastructure investment.
- Year-on-year FAI growth declined by 4.5 percentage points to 15.4% in May on the higher-base effect. On a 2020-21 average basis, FAI growth continued to accelerate from 3.9% through April to 4.2% through May. However, the month-on-month growth slowed to 0.17% from 1.49% in April. By sector, the headline improvement was entirely driven by accelerations in investment in manufacturing. Manufacturing investment returned to expansion of 3.7% on a 2020-21 average basis, compared with a 0.4% contraction in April. High-tech manufacturing, driven primarily by the strength in IT, medicine, and medical instruments manufacturing, continued to report double-digit growth on a two-year (2020-21) average basis. However, real estate investment growth fell by 1.3 percentage points to 9% on a two-year (2020-21) average basis compared with the April level, and infrastructure investment continued to slow to 3.4% from 3.8% in April on a two-year (2020-21) average basis.
- Despite the deceleration in real estate investment, construction and installation activity remained relatively stable or even stronger. On a 2020-21 average basis, floor space of new starts contracted at a slower pace, and floor space under construction and completed only marginally reduced from April. This contradiction partially reflects the impact of the land provision reforms.
- Year-on-year nominal retail sales growth fell by 5.3 percentage
points from April down to 12.4% in May. On a two-year (2020-21)
average basis, retail sales growth rose by 0.2 percentage point
from April to 4.5% in May, but the figure remains far below the
8.6% y/y growth registered in May 2019.
- Mainland China's average new home prices increased by 0.52%
month on month (m/m) in May, compared with 0.48% m/m in April,
according to the survey conducted by the National Bureau of
Statistics covering 70 major cities. (IHS Markit Economist Lei Yi)
- The minor uptick in month-on-month new home price inflation in May was broad across all three city tiers, led by tier-1 and tier-3 cities. Among the four tier-1 cities, Guangzhou continued to report the highest new home price inflation of 1.5% m/m, up by 0.4 percentage point from the April reading.
- Month-on-month new home price inflation inched up by 0.1 percentage point for Shanghai and Shenzhen in May, but declined by 0.3 percentage point in capital city Beijing. Up to 62 out of the 70 surveyed cities registered month-on-month new home price gains, unchanged from March and April.
- Chinese internet giant Baidu through its smart driving unit Apollo plans to offer robotaxi services to 3 million users in China in 2023. To achieve this, the company plans to deploy 3,000 robotaxis, reports Reuters. Baidu also announced a collaboration with BAIC Group's ARCFOX electric vehicle (EV) brand to build the Apollo Moon, an EV robotaxi that would be mass-produced for CNY480,000 (USD74,986) per unit. In the next three years, the companies jointly plan to develop 1,000 Apollo Moon EVs. (IHS Markit Automotive Mobility's Surabhi Rajpal)
- Hyundai Motor Group's dedicated fuel-cell system brand, HTWO, will provide its fuel-cell generator to the Electric Touring Car Racing (ETCR) category, according to a company press release. ETCR is the world's first all-electric touring car race category, which provides leading automakers with a global stage to showcase their electric technology in a high-performance arena. Only vehicles without internal combustion engines are allowed to participate. Pure ETCR races will be held for the first time in Vallelunga (Italy) from 18 to 20 June. Hyundai Motor Group is not only entering its own racing team in the Pure ETCR championship but is also providing a mobile charging infrastructure that uses HTWO's proprietary fuel-cell generator to charge all participating high-performance EVs. The charging system can generate up to 160 kW of electricity, boasting an output equivalent to twice that of the Nexo, Hyundai's fuel-cell electric vehicle (FCEV). The system can fully charge two ETCR vehicles - each equipped with a 65-kWh battery - simultaneously within an hour. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Jamal Amir)
S&P Global provides industry-leading data, software and technology platforms and managed services to tackle some of the most difficult challenges in financial markets. We help our customers better understand complicated markets, reduce risk, operate more efficiently and comply with financial regulation.
This article was published by S&P Global Market Intelligence and not by S&P Global Ratings, which is a separately managed division of S&P Global.
