Daily Global Market Summary - 28 July 2020
Equity markets closed mixed across APAC and Europe, while all major US equity indices closed lower. iTraxx and CDX closed wider across IG and high yield and Brent/WTI was also weaker on the day. US government bonds rallied on July's decline in US consumer confidence, despite data indicating that the growth rate of new COVID-19 cases appears to be declining in the US.
Americas
- US equity markets closed lower and close to the nadir of the day; Nasdaq -1.3%, Russell 2000 -1.0%, DJIA -0.8%, and S&P 500 -0.7%.
- 10yr US govt bonds closed -3bps/0.58% yield and 30yr bonds -4bps/1.22% yield.
- CDX-NAIG closed +2bps/72bps and CDX-NAHY +3bps/455bps.
- Gold closed +0.7%/$1,944 per ounce to yet another new all-time high close and had reached another record intraday high of $1,974 per ounce overnight.
- Crude oil closed -1.3%/$41.04 per barrel.
- Coronavirus cases in the U.S. climbed 1% as compared with the same time Monday to 4.31 million, according to data collected by Johns Hopkins University and Bloomberg News. The increase was below the average 1.7% daily gain over the past week. Deaths rose 0.7% to 148,298. (Bloomberg)
- The US Conference Board Consumer Confidence Index fell 5.7
points (5.8%) to 92.6 in July after a 12.4-point jump in June. The
June reading had reflected hopes for a speedy economic recovery as
states reopened for business, but in mid-July COVID-19 cases were
surging past their previous highs and it was clear that such
optimism was premature. The July reading is consistent with our
expectation of slower monthly growth in consumer spending in the
third quarter than in May and June. (IHS Markit Economists David
Deull and James Bohnaker)
- The present situation index advanced 7.5 points to 94.2, not enough to offset a 14.6-point retrenchment in the expectations index to 91.5.
- Views on the present situation for both employment and business conditions improved in July. The labor index (the percentage of respondents viewing jobs as plentiful minus the percentage viewing jobs as hard to get) increased 4.1 points to 1.3, about its level as of mid-2016.
- The plunge in the expectations index brought it to the lowest level since March as consumers came to appreciate that the COVID-19 virus will remain a major threat to public health and a drag on business activity into the fall and beyond. In its press release, the Conference Board noted that declines were large in Florida, Texas, and California, states where the surge in cases has been particularly pronounced.
- The net share of respondents expecting business conditions to improve in six months fell 14.9 percentage points to 12.3%. A net 10.3% expected employment conditions to improve, down 13.7 percentage points from June.
- Purchasing plans were mixed in July. The share of respondents planning to buy autos in the next six months fell 0.4 percentage point to 11.5%, and the share planning to buy major appliances fell 2.1 points to 43.5%. The share planning to buy homes, however, increased 0.6 percentage point to 7.4%, matching its highest level since 2006. Record-low mortgage rates and a shift toward living situations conducive to social distancing have made homebuying a more attractive prospect.
- The US homeowner vacancy rate, the proportion of residential
inventory vacant and for sale, dropped four ticks in the second
quarter from a year earlier, to 0.9%—this was the lowest
second-quarter reading since 1986. (IHS Markit Economist Patrick
Newport)
- Nearly every estimate in the release is tainted. The key flaw was that the Census suspended in-person interviews, replacing them with telephone interviews. According to a FAQ, the Census Bureau went out of its way to track down phone numbers. This was insufficient to keep the response rate from plummeting to 67%, 12 percentage points below the year-earlier value and 13 percentage points down from the first quarter. Response rates fell progressively from 83% in February to 73% in March, 70% in April, 67% in May, and 65% in June.
- The rental vacancy rate, the proportion of rental inventory vacant and for rent, dropped to 5.7%, from 6.8% a year earlier. This was the lowest reading since the second quarter of 1984.
- The homeownership rate soared to 67.9%, from 64.1% four quarters earlier.
- The seasonally adjusted homeownership rate jumped 2.9 percentage points from the first quarter to 68.2%—the highest reading since the third quarter of 2007.
- Estimated housing inventory increased to 140.362 million, up 1.153 million year over year.
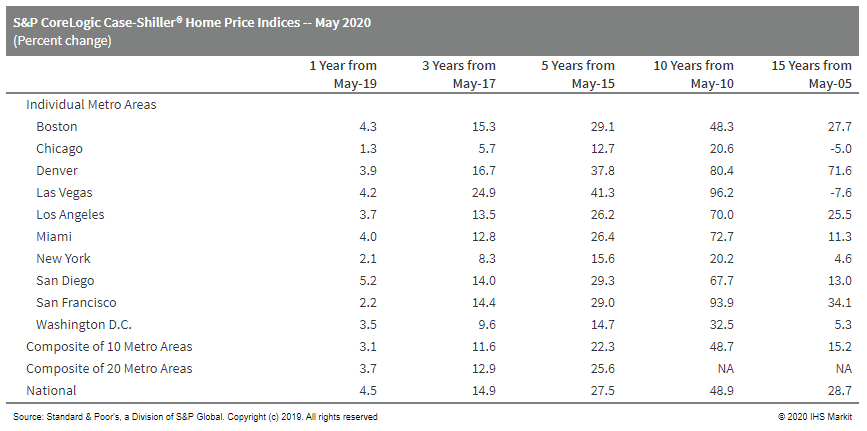
- The S&P CoreLogic Case-Shiller composites decelerate
slightly in May but US home price growth remains strong. (IHS
Markit Economist Troy Walters)
- For the third month in a row, data in May were limited to only 19 cities as opposed to 20 under normal circumstances. Data for Wayne County, Michigan, were unavailable and as a result, there are no data for Detroit in this release.
- Both the 10-city and 20-city composite indices were flat month over month (m/m) in May.
- Home prices were up month on month (m/m) in 11 of the 19 cities reported. Increases ranged from 0.1% in Boston, Miami, Portland, and Washington, DC, to 0.6% in Phoenix. Prices fell in Las Vegas (down 0.1%), Minneapolis (down 0.7%), New York (down 0.1%), Seattle (down 0.2%), and San Francisco (down 0.5%).
- On an annual basis, home price growth slowed in May. The 10-city index was up 3.1% year on year (y/y), slower than April's reading of 3.3%. The 20-city index was up 3.7% y/y compared to 3.9% in April.
- Despite decelerating, y/y price growth in May remained well into positive territory, with prices higher than one year ago in all 19 cities reporting. Increases ranged from 9.0% in Phoenix to just 1.3% in Chicago.
- Growth in the national index slowed slightly to 4.5% y/y in
May.
- Eastman Kodak Co. has won a $765 million government loan from the U.S. International Development Finance Corporation under the Defense Production Act, the first of its kind. The purpose of the loan is to help expedite domestic production of drugs that can treat a variety of medical conditions and loosen the U.S. reliance on foreign sources. (WSJ)
- The Federal Reserve is extending the emergency lending facilities it set up to shore up financial markets during the pandemic from September to the end of this year, in the latest sign of its concern that the coronavirus crisis will continue to weigh on the US economy. (FT)
- Volkswagen (VW) has announced that the expansion of its California testing facility is complete, with facilities focused on powertrain engineering services. The facility is located in Oxnard, creating the Oxnard Engineering Campus (OEC). OEC is on nine acres, holding design and testing space. The center is intended to support VW brands including VW, Audi, Bentley, and Porsche - all offered in North America. The powertrain engineering services will support product development, governmental compliance and emissions testing. OEC will have an enhanced focus on electric vehicle (EV) range testing and analysis, according to a VW statement. The OEC actually comprises three different centers, the Test Centre California (TCC), VW Quality and Audi Engineering, and Design Centre California (DCC). The DCC takes a new home as part of the OEC, moving from a prior location in Santa Monica, California. Johan de Nysschen, COO for VW Group of America, is quoted as saying, "The next few years are going to be transformative for the Volkswagen Group as we are introducing our first long-range battery electric vehicles. The campus has been completely upgraded to further support the successful development, design and testing of products that will be sold in this market." (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Stephanie Brinley)
- COAST Autonomous has selected LeddarTech's Leddar Pixell Cocoon LiDAR sensor for its autonomous delivery vehicle, according to a company statement. The vehicle will be deployed at the Kinney County Railport (KCRP) in Texas (United States) to autonomously operate and move equipment and supplies. LeddarTech claims that its Cocoon LiDAR is designed to create a 360-degree cocoon to provide enhanced collision prevention in autonomous vehicles. Pierre Lefevre, chief technology officer at COAST Autonomous, said, "It has been a great opportunity to deploy vehicles at KCRP. The railyard is the perfect environment to show how autonomous vehicles function, particularly in an industrial environment, keeping the workforce safer and improving efficiency by allowing them to focus on more highly skilled tasks". COAST Autonomous develops vehicle automation and monitoring systems that transform vehicles into driverless shuttles. The company has also developed an autonomous shuttle, named COAST P-1, which does not have pedals or a steering wheel. Its electric wheel hub motors allow it to achieve speeds of up to 25mph, and it has a maximum capacity of up to 20 passengers. The shuttle can also be reconfigured to be used as a delivery vehicle. It can be hailed via a smartphone application and determines its best route using COAST's mapping software. (IHS Markit Automotive Mobility's Surabhi Rajpal)
- The volume of the treated area of agrochemicals rose by some 7% in the first three months in Brazil. The national crop protection association, the Sindiveg, reported that equivalence treated area (PAT), which calculates the volume use by treated area, was up during the first quarter and increased from 513 million ha to 550 million ha equivalent. That followed a year in which Latin America's agrochemical market bucked the global trend in 2019, rising 8% while other regions saw sales drop. However, one study revealed a big drop in imports from China in the early months of 2020. Imports were down 40% from China. Imports from China and India combined fell by 28% to $199 million, of which $69 million came from China. There was a switch towards sourcing from Europe, reflecting a likely effect of shutdowns due to the pandemic. Imports from the continent rose by 10% to $102 million. Imports from the US were stable at some $154 million. That contrasted with trade picture for 2019. The impact of the ongoing trade war between China and the US seems to be reflected in the values exported to various destinations from China. Unlike previous years, the US was not the top destination for Chinese exports during the first three quarters of 2019. Brazil was the top destination with $1,027 million worth of pesticides being exported there. The US followed with $846 million. The picture contrasts with 2018, when $1,314 million worth pf pesticides were exported to the US and $988 million worth to Brazil. (IHS Markit Crop Science's Robert Birkett)
Europe/Middle East/ Africa
- European equity markets closed mixed; Spain +1.1%, UK +0.4%, Germany flat, France -0.2%, and Italy -0.6%.
- 10yr European govt bonds closed mixed; Italy +3bps, Spain +1bp, UK flat, France -1bp, and Germany -2bps.
- iTraxx-Europe closed +1bp/60bps and iTraxx-Xover +6bps/365bps.
- Brent crude closed -0.7%/$43.60 per barrel.
- The Spanish employment recovery ended abruptly in the first
half of 2020. Employment shrunk for a second successive quarter
when falling by 6.7% quarter on quarter (q/q) during the second
quarter of 2020 after a 0.4% q/q in the first, the first drop since
late 2013. (IHS Markit Economist Raj Badiani)
- The latest labor market indicators show a significant hit from the COVID-19 virus, namely the impact of a lengthy lockdown of the economy during March and part of the second quarter.
- According to the national statistical office (INE), employment shrunk markedly during the second quarter of 2020. On an annual basis, total employment fell by 6.1% year on year (y/y), or by 1.2 million jobs to 18.6 million, the first drop since early 2014. This compares to gains of 1.1% y/y in early 2020, 2.3% in 2019 and 2.7% in 2018.
- A breakdown by economic activity reveals that services endured the sharpest job losses in the second quarter, down by 6.2% y/y (922,200 new jobs) to 14.9 million. Industry employment was 4.4% lower y/y, implying 122,200 fewer jobs to stand at 2.6 million.
- Firms shed workers on temporary contracts, which decreased by 21.1% y/y or 0.9 million to 3.5 million during the second quarter, dwarfing the loss of permanent jobs (down 1.9% y/y). Spain has a high incidence of temporary employment, which reflects dense job protection legislation for permanent workers.
- On a seasonally adjusted basis, employment shrunk for a second successive quarter when falling by 6.7% quarter on quarter (q/q) during the second quarter after a 0.4% q/q in early 2020, the first drop since late 2013. This matched IHS Markit's estimate for the second quarter.
- The INE notes that the public health measures to contain the COVID-19 virus have had an even larger negative impact on the employment level because workers suspended via the Temporary Suspension of Employment (ERTE) are recorded as employed. The ERTE scheme allows firms to suspend employment, with workers able to apply for unemployment benefits during the time of their suspension.
- Meanwhile, the number of unemployed people increased by 4.3% y/y to stand at 3.4 million during the third quarter. Therefore, the unemployment rate increased to 15.3% in mid-2020, up from 14.0% a year ago.
- INE reports that over a million people lost their jobs during the second quarter but are not classified as unemployed since they did not meet the technical conditions to be included in this group, such as still actively seeking work. Therefore, the number classified as inactive rose by 8.7% y/y or by 1.4 million, or the activity rate fell.
- Boehringer Ingelheim Animal Health has bolstered its regenerative medicine capabilities with the acquisition of Global Stem cell Technology (GST). GST is a Belgian veterinary biotechnology firm focused on the research and development of stem cell therapies to treat orthopedic and metabolic diseases in animals. Financial details of the deal have not been disclosed. The acquisition of GST follows a two-year partnership that led to the first ever authorization and market launch of a stem cell product for animal health in Europe. Boehringer launched Arti-Cell Forte in April 2019, for the reduction of mild to moderate recurrent lameness associated with non-septic joint inflammation in horses. Boehringer first signed an exclusive European distribution deal with GST for Arti-Cell Forte in June 2018, after the therapy received a landmark positive opinion. A spokesperson for Boehringer told IHS Markit Animal Health the company expects the integration of GST to accelerate the market launch of Arti-Cell Forte in other territories. (IHS Markit Animal Health's Sian Lazell)
- A new three-year loan deal with the International Monetary Fund
(IMF) will provide Moldova with crucial funding as it struggles
with the impact of the COVID-19 virus pandemic. (IHS Markit
Economist Sharon Fisher)
- The IMF announced on 27 July that a staff-level agreement has been reached with the Moldovan authorities on three-year Extended Credit Facility and Extended Fund Facility (ECF/EFF) arrangements. Replacing a previous three-year agreement from November 2016, the new program aims to push forward institutional reforms and support Moldova's post-pandemic recovery.
- Moldova has struggled to contain the spread of the pandemic, and the country had 23,154 confirmed cases as of 27 July, with 748 deaths. Public finances have deteriorated markedly, with the central government deficit nearly doubling in the first half of 2020.
- If approved by the IMF's Executive Board, the ECF/EFF loan would give Moldova access to approximately USD558-million-worth of financial assistance. The IMF loan deal would also open the door to funding from other international donors.
- The IMF's Executive Board is expected to consider Moldova's loan agreement in September, and approval depends on the implementation of a number of policy actions related to central bank independence, oversight of the financial sector, and fiscal transparency. Key priorities for institutional reform over the next three years include fiscal governance, oversight of the non-bank financial sector, market regulation, rule of law, and tackling corruption.
- The International Monetary Fund (IMF) has approved South
Africa's request for USD4.3 billion in emergency financing under
the Rapid Financing Instrument (RFI). Although the relatively
limited IMF conditionalities have been downplayed by local
politicians, the potential benefits of adhering to the IMF
guidelines should not be underestimated by the government. (IHS
Markit Economist Thea Fourie)
- The IMF has approved USD4.3 billion of financial assistance to South Africa under the RFI, amounting to 100% of South Africa's quota. On 22 June, the Africa Development Bank (AfDB) approved a USD304-million loan to the South African government, in support of the government's efforts to mitigate the social and economic impacts stemming from the COVID-19 pandemic.
- A statement that accompanied the IMF's RFI approval outlines that the funding will be used to address pressing balance-of-payments needs originating primarily from the fiscal pressures in the South African economy, to limit regional pandemic spillover effects, and, it is hoped, catalyze additional financing from other international financial institutions.
- Remittance inflows to Kenya remained resilient during the first
five months of 2020, latest statistics from the Central Bank of
Kenya (CBK) show. Remittances from North America, accounting for
53% of total remittance inflows, grew by 13.1% year on year (y/y)
during the first five months of 2020, offsetting a 30.3% y/y
contraction in remittances from Europe. Overall remittance inflows
to Kenya increased by 1.7% y/y during the first five months of
2020. (IHS Markit Economist Thea Fourie)
- The impact of global travel restrictions amid the COVID-19 pandemic has been detrimental for Kenya's tourism sector. Foreign tourist arrivals to Kenya contracted by 20.2% y/y during the first quarter of 2020, numbers from the Kenya National Bureau of Statistics (KNBS) show. The drop in foreign tourist arrivals in March accelerated to average a massive 59.1% y/y.
- A fall in Kenya's trade deficit and resilient remittance inflows left Kenya's overall current-account deficit at USD1,088 million during the first quarter of 2020, down from USD1,673 million in the fourth quarter of 2019, latest statistics of the KNBS show. Low import demand amid higher exports were primarily responsible for the improvement in the trade deficit.
- Inflows on the capital and financial account moderated to USD445 million during the first quarter of 2020, from USD1.375 billion in the fourth quarter of 2019, allowing for a fall in Kenya's total foreign-reserves holdings by USD472 million to USD12.4 billion (or 5.2 months of imports of goods and services) by the end of March 2020. The build-up of global COVID-19-related uncertainties during the first quarter resulted in a sharp reversal of capital flows to developed economies.
- Kenya's total exports rebounded during May and June, the CBK reported, driven primarily by tea, horticultural products and re-exports. "Horticulture exports are almost at normal levels, mainly due to a pickup in demand and easing of supply restrictions in key destination markets, and increased cargo capacity," the CBK reported.
- Kenya's real GDP remained strong, increasing by 4.9% y/y during the first quarter, the KNBS reported. The Kenyan economy gained from strong growth in the agricultural and fishing industries, followed by the manufacturing and services sectors. Output in the accommodation and food services sector - the first sector to be impacted by the COVID-19 pandemic - contracted by 9.2% y/y over the period.
- Five new members were appointed to electricity distribution and
transmission utility Kenya Power and Lighting Company's (KPLC)
board on 20 July, after the majority shareholder, Kenya's Treasury,
forced the previous members to resign a week previously. (IHS
Markit Country Risk's William Farmer and Eva Renon)
- In June, KPLC issued a third consecutive annual profit warning, projecting annual earnings would fall by 25%.
- The previous year, net earnings fell by 92%. The recurrent balance-sheet issues stem from high power purchase costs and subsidized connections for rural communities. KPLC has faced corruption and fraud investigations, with senior managers arrested in 2019 for alleged tendering fraud, and over 100 employees were dismissed in 2019 for their alleged involvement in electricity theft.
- As a result of the lockdown and curfew measures introduced in response to the COVID-19 virus pandemic, electricity demand has fallen by 8%, according to state-owned Kenya Electricity Generating Company.
- Consequently, in June, KPLC issued force-majeure notices to 10 independent power producers (IPPs). The IPPs have complained that reduced demand does not constitute a valid justification to negate their power purchasing agreements, raising the possibility of a legal challenge.
- Treasury Secretary Ukur Yatani has seen through budget rationalization measures since his appointment in July 2019, so the Treasury's leadership at KPLC is likely to drive efficiency improvements.
- This would include efforts to reduce transmission and distribution losses, which KPLC estimated at 24% over 2019.
Asia-Pacific
- APAC equity markets closed mixed; South Korea +1.8%, India +1.5%, China/Hong Kong +0.7%, Japan -0.3%, and Australia -0.4%.
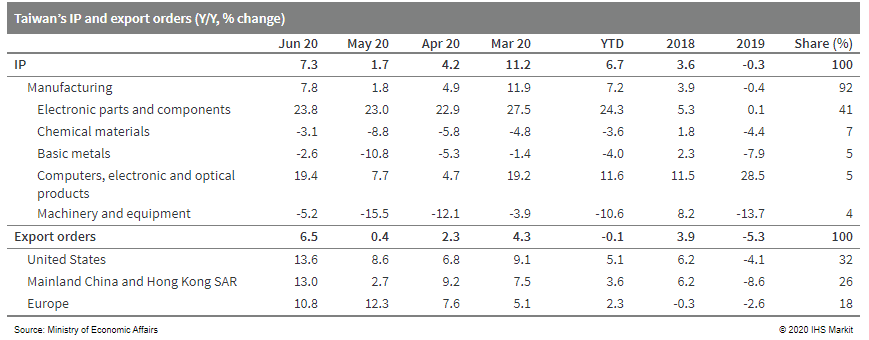
- Taiwan's export orders and industrial output expanded at a
faster pace in June as demand for electronics and information and
communication products continued to surge during the month, which
provided the key driving force and which was bolstered by booming
demand for distance working and learning. That said, the resurgence
of COVID-19 infections around the world and the resulting
increasing uncertainties to global demand have prompted the
government to step up its effort to stimulate the economy with
additional budget in July. (IHS Markit Economist Ling-Wei Chung)
- Taiwan's cabinet added an extra special budget to its COVID-19 relief fund in late July to combat the pandemic and provide needed support to hard-hit sectors. The total of relief fund to date amounted to TWD420 billion (USD14.2 billion).
- The initial relief package was announced in February with the amount of TWD60 billion, which was followed by the first supplementary budget announced in April with the total of TWD150 billion. As the pandemic shows no signs of easing globally, the cabinet announced the second supplementary budget in late July with the amount of TWD210 billion, including TWD38.3 billion allocated to fight against the spread of the virus and TWD171.7 billion on bailout and measures to support the economy.
- By ministries, the bulk of the second extra budget - TWD137.6 billion - will be allocated to the Ministry of Economic Affairs. It includes TWD45.0 billion on supplementary for business loans, TWD38.2 billion on discount coupons (Triple Stimulus Vouchers), and TWD37.8 billion on subsidies for trade services sector, exhibition-related sector, and manufacturing sector.
- Export orders - representing a leading indicator of actual exports - expanded for the fourth straight month in June, rising by 6.5% year on year (y/y), accelerating from a just 0.4% y/y gain in May. It also represented the fastest increase since August 20218.
- Orders of electronic products remained the key driver of expansion, surging 23.9% y/y in June, while orders of information and communication products continued to climb as well, up 17.1% y/y. The technology sectors continued to benefit greatly from booming demand for products and equipment related to working from home and remote education.
- Non-technology sectors remained lagged behind as they continued to suffer from plunging demand, hit hard by the adverse effect of the pandemic. That said, although still declining at a double-digit pace, a pick-up in international oil and raw material prices helped narrow the contractions.
- By markets, orders from the US, mainland China, Hong Kong SAR, and Europe expanded at a double-digit pace, boosted mainly by booming technology demand. These helped offset shrinking orders from Japan and still-sluggish demand from ASEAN.
- Concurrently, supported by rising export orders, IP strengthen
in June as well, increasing 7.3% y/y, accelerating from a 1.7% y/y
gain in May. Surging technology production continued to lead the
expansion in June, while the narrower declines in the
non-technology production helped the acceleration in overall
manufacturing production during the month.
- The enticement of lower costs could accelerate the unleash of
pent-up travel demand in the second half, boosting tourism spending
and in turn stabilizing employment in related sectors. Renewed
regional case surges remain the major headwind for a sustained
pickup. (IHS Markit Economist Lei Yi)
- Mainland China's Ministry of Culture and Tourism (MCT) lifted the ban on interprovincial group tours on 14 July, after a nearly six-month shutdown since late January. Following this, local governments have started rolling out ticket price discounts to attract more tourists for spurring tourism consumption.
- Shandong issued a notice on 24 July, lowering ticket prices for 81 state-owned tourist sites in the region by 50-80% from August until the end of 2020, according to the provincial development and reform commission and cultural and tourism department.
- Similarly, Shanxi announced on 18 July to waive admission tickets on workdays for 126 local tourist attractions in the second half of 2020. To cover the income loss, fiscal subsidies of no less than 20% will be provided both at the provincial and municipal level.
- IHS Markit has downgraded Fiji's medium-term sovereign risk
rating to B+ (55/100 on IHS Markit's numerical scale), from BB-
(50), and returned the outlook to Stable. This is due primarily to
extreme current-account pressures caused by the collapse of tourism
revenues in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic. (IHS Markit
Sovereign Risk's Andrew Vogel)
- Given Fiji's economy is already lacking diversity and its agricultural and manufacturing sectors have weak competitiveness, the small island country is heavy reliant on tourism exports and transportation services for maintaining a current-account surplus. The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic is putting extraordinary pressure on the country's economy as travel restrictions and containment measures disproportionately affect its services exports.
- As the pandemic progresses, the scenario of a quick recovery for tourism exports and related services has become less likely. Given the short-term losses suffered will already translate to permanent losses in the medium- and long-term, any further weakness in the tourism sector would add additional pressure to the country's medium-term liquidity risks.
- Fiji is also very import dependent and, with potential stimulus measures being undertaken along with recovery efforts from April's Cyclone Harold, room for the country to reduce spending is quite small, leaving Fiji's liquidity position in a weakening position and elevating its overall risk.
S&P Global provides industry-leading data, software and technology platforms and managed services to tackle some of the most difficult challenges in financial markets. We help our customers better understand complicated markets, reduce risk, operate more efficiently and comply with financial regulation.
This article was published by S&P Global Market Intelligence and not by S&P Global Ratings, which is a separately managed division of S&P Global.
