Daily Global Market Summary - 4 August 2020
Equity markets closed higher across most of the globe and benchmark government bonds were also higher on the day. Commodities remained strong, as gold reached another record high today and oil also closed higher. iTraxx/CDX indices closed modestly tighter across both IG/high yield. The market will likely be focusing on this Friday's US employment report for the remainder of the week to assess how much the current wave of COVID-19 infections are impacting the restoration of the job losses from the initial wave.
Americas
- US equity markets closed modestly higher; Russell 2000 +0.7%, DJIA +0.6%, and Nasdaq/S&P 500 +0.4%.
- 10yr US govt bonds closed higher today at -5bps/0.51% yield and 5yr bonds closed at -3bps/0.19% yield after reaching a new record low intraday yield of 0.18%.
- CDX-NAIG closed -1bp/66bps and CDX-NAHY -3bps/430bps.
- Gold closed at +1.7%/$2,021 per ounce, which is a new record high close and it also broke a new intraday all-time high of $2,037 per ounce.
- Crude oil closed +1.7%/$41.70 per barrel.
- Coronavirus cases in the U.S. increased 1.1%, as compared with the same time Monday, to 4.74 million, according to data collected by Johns Hopkins University and Bloomberg News. The increase was lower than the average 1.4% daily gain over the past week. Deaths rose 0.7% to 156,133. (Bloomberg)
- US Manufacturers' orders rose 6.2% in June, while shipments
rose 9.8%. Both followed increases in May. Inventories also rose in
June on the heels of an increase in May. The data in this report
reveal a manufacturing sector in the midst of recovery—at least
through June.(IHS Markit Economists Ben Herzon and Lawrence Nelson)
- The details in this report that bear on our GDP tracking added 0.1 percentage point to our forecast of third-quarter GDP growth, which now stands at 20.4% (annual rate). Our estimate of second-quarter GDP growth is unrevised at a 32.9% annualized rate of decline.
- The increase in new orders in June reflected increases in both durables and nondurables. Most of the increase in durables was in transportation equipment.
- Most of the increase in new orders for nondurable goods (which are assumed equal to shipments of nondurable goods), was in petroleum refineries, where petroleum prices have been rebounding.
- The increases in new orders over May and June reversed roughly one-half of the decline in orders over March and April, as the recovery in manufacturing has a ways to go.
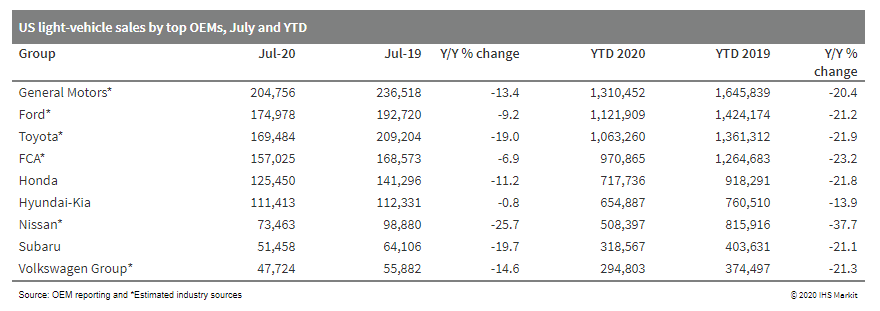
- US light-vehicle sales are estimated to have dropped 12.2% year
on year (y/y) to 1,227,420 units in July and decreased 21.8% y/y to
7,688,741 units in the year to date (YTD). The seasonally adjusted
annual rate (SAAR) of US light-vehicle sales is estimated to be
14.1-14.5 million units in July. Although remaining well below the
year-earlier levels, light-vehicle sales in July are expected to
have improved from the month prior reading and reflect little
immediate impact from rising counts of COVID-19 cases in some US
regions. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Stephanie Brinley)
- Argo AI, an autonomous and artificial intelligence (AI) technology company has reached a valuation of USD7.5 billion, reports TechCrunch. This official valuation was confirmed nearly two months after the Volkswagen (VW) Group finalized its USD2.6-billion investment in Argo AI (see United States: 3 June 2020: VW finalizes investment in autonomous tech company Argo AI). The deal was reached in July 2019 (see United States - Germany: 15 July 2019: VW to expand Ford partnership, plans to invest USD2.6 bil. in Argo AI), and Ford and VW will share equal ownership stakes in Argo AI. Argo AI's present valuation is just a little more than in 2017 when Ford invested USD1 billion into it. Ford has tested its autonomous vehicles (AVs) in Miami in partnership with Domino's (for pizza delivery) and Walmart and Postmates (for goods delivery). It has also tested its AV fleet in Washington, DC and announced that Austin will be the third city for which it has targeted commercial deployment of its AVs. (IHS Markit Automotive Mobility's Surabhi Rajpal)
- Walt Disney Co. posted its first quarterly loss since 2001, nearly $5 billion, as the majority of its business segments reeled from government efforts to corral the coronavirus by shutting down public spaces around the world. The COVID-19 pandemic has closed Disney's theme parks, virtually eliminated movie distribution and curtailed live sports, a key programming source for Disney TV networks. However, the world's shut-in nature has helped the company's Disney+ streaming service secure more than 60 million users in nearly nine months, a mark that Netflix took about eight years to achieve. (WSJ)
- LyondellBasell's revenue totaled $5.546 billion, down 39% YOY
from $9.048 billion. Adjusted earnings per share dropped 74% YOY to
71 cents while beating the average analyst estimate of 65 cents as
compiled by Refinitiv. (IHS Markit Chemical's Clay Boswell)
- The olefins & polyolefins - Americas segment turned in adjusted EBITDA of $210 million, down from $635 million in the year-ago period. Olefins results declined about $235 million YOY as lower coproduct prices cut into ethylene margin, and lower demand cut into ethylene volume.
- The olefins & polyolefins - Europe, Asia, International segment turned in adjusted EBITDA of $219 million, down from $331 million in the year-ago period. The olefins contribution declined about $90 million. Lower ethylene prices were partially offset by lower feedstock costs, while lower demand pulled down volume.
- The intermediates and derivatives segment reported adjusted EBITDA of $121 million, down from $448 million. The contribution from propylene oxide & derivatives dropped about $40 million on reduced demand and lower margins.
- The advanced polymer solutions segment turned in adjusted EBITDA of $23 million. Costs related to the integration of A. Schulan were relatively unchanged YOY.
- The refining segment reported adjusted EBITDA of a $14-million loss, compared to a $66-million loss in the year-ago period. Coke and sulfur co-product prices kept up with crude price and hedge gains, while the Maya 2-1-1 industry benchmark crack spread declined $5.73/barrel. Crude throughput decreased by 24,000 b/d owing to unplanned maintenance in the first weeks of April 2020 and second-quarter rate reductions tied to low demand for refined products.
- The technology segment turned in adjusted EBITDA of $112 million, up YOY from $107 million. Catalyst volumes and margins increased on customer inventory stocking early in the pandemic; licensing revenue declined.
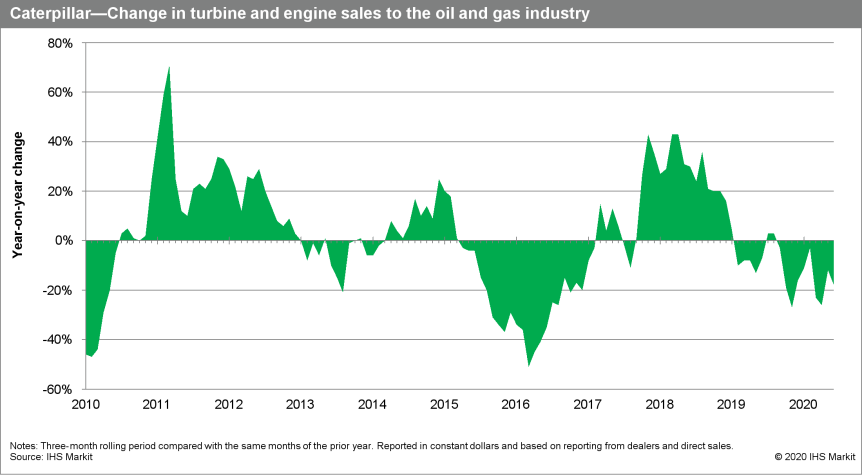
- Caterpillar has announced that Energy & Transportation's
revenue declined by 24% year on year (y/y) in the second quarter of
2020 to USD4.1 billion. Sales declined across all applications and
inter-segment engine sales. In the Oil and Gas business area sales
decreased mainly because of lower demand in North America for
reciprocating engines used in gas compression and decreased sales
of engine aftermarket parts, partially offset by higher sales of
turbines and turbine-related services. In the Power Generation
business, sales decreased primarily due to lower sales volume in
small reciprocating engine applications and engine aftermarket
parts. Industrial business' sales decreased on lower demand across
all regions, while Transportation business' sales declined in rail
because of lower deliveries of locomotives and related services and
in marine applications, primarily in EAME and Asia/Pacific. Energy
& Transportation's operating profit declined by 30% y/y to
USD624 million in the second quarter of 2020 mostly due to lower
sales volume. The decline was partially offset by lower expenses in
areas such as sales, general administration, R&D, and
manufacturing. (IHS Markit Upstream Costs and Technology's Kamila
Langklep)
- Colombia's central bank voted on 31 July to cut interest rates
from 2.5% to 2.25%; the interest rate was stable at 4.25% between
May 2018 and January 2020. This move represents the fifth
consecutive cut. IHS Markit forecasts one more rate cut so that
rates reach 2% by year-end. (IHS Markit Economist Ellie Vorhaben)
- The Central Bank of Colombia (Banco de la República: Banrep) has been able to aggressively cut interest rates since inflation is low and continues to decline, reaching 2.2% in June (2% core), well below the targeted rate of 3%. Expectations are declining as well, and the bank's technical team now expects inflation to be between 1% and 2% for the rest of the year.
- The bank highlighted the importance of labour market indicators in making its decision. IHS Makit agrees with the bank's analysis that the worst of the economic shock occurred during the second quarter. During the first half of the year, the Colombian economy lost 5.4 million jobs, equal to a 24% decline in the employed population.
- The bank noted improving financial market conditions, improved liquidity, and lower foreign-exchange volatility. The Colombian peso has been making gains for the past three months on the basis of improving oil prices (although are still weak compared with the beginning of 2020).
Europe/Middle East/ Africa
- Most European equity markets closed higher except for Germany -0.4%; Italy +1.2%, Spain +0.7%, France +0.3%, and UK +0.1%.
- 10yr European govt bonds closed sharply higher; Spain/Italy -6bps, France/Germany -3bps, and UK -2bps.
- iTraxx-Europe closed -1bp/57bps and iTraxx-Xover -9bps/353bps.
- Brent crude closed +0.5%/$44.35 per barrel.
- HICP inflation in the eurozone edged up from 0.3% to 0.4% in
July, according to Eurostat's 'flash' estimate, the second
successive modest acceleration, although headline and core rates
remain well below the European Central Bank's (ECB)'s "below but
close to 2%" objective. (IHS Markit Economist Ken Wattret)
- Upward pressure on the inflation rate for energy again contributed to the pickup, reflecting the lagged impact of higher oil prices, although the energy rate remained deeply negative nonetheless (at -8.3%).
- Food inflation also continued its recent deceleration, slipping from 3.2% to 2.0% in July. The slowdown has been primarily driven by unprocessed food, where the inflation rate has more than halved recently to 3.2% in July versus April's 7.6% peak.
- The big surprise in July's HICP release was the unexpected jump in the inflation rate excluding food, energy, alcohol, and tobacco. It rose from 0.8% to 1.2%, its highest level since February.
- Notably, services inflation (which accounts for around two-thirds of the core measure above) decelerated again in July, from 1.2% to just 0.9%, the lowest rate since April 2016 and well below the recent peak of 1.9% in November 2019.
- The reason for the jump in core inflation in July was a rise in non-energy industrial goods inflation from 0.2% to 1.7%. This was by far the largest one-month acceleration in the series' history.
- The primary reason for the jump in non-energy industrial goods inflation in July was the postponement of sales discounts in some European countries, including France, Italy, and Belgium. We expect this effect to unwind in August's HICP release, leaning back down on the core inflation rate.
- A 'flash' estimate released by Statistics Portugal show GDP
declining by 14.1% quarter on quarter (q/q) during the second
quarter. Output had declined by 3.8% q/q during the first three
months of 2020. (IHS Markit Economist Diego Iscaro)
- On a year-on-year (y/y) basis, GDP declined by 16.5% during the second quarter. As a reference, the largest y/y decline in GDP during the financial and sovereign debt crises was 4.5% during the fourth quarter of 2012.
- Statistics Portugal did not release a component breakdown alongside the 'flash' GDP estimate. However, it mentions that the quarterly decline in activity was largely the result of collapsing domestic demand, although net exports also made a negative contribution.
- Figures also released by Statistics Portugal show industrial production growing by 11.2% month on month (m/m) in June, following a fall of 20.9% m/m in April and an increase of 2.7% m/m in May. Industrial production still fell by 22.1% q/q during the second quarter.
- Production in June was still 17.4% below its pre-coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) virus pandemic level in February (see chart). Production of intermediate goods was almost 20% below its February level despite growing by 7.6% m/m in June. Production of consumer durables increased by almost 50% m/m in and stood 12.8% below its level in February.
- The Portuguese passenger car market has declined again in July, although at a slower rate. According to the latest data published by the Automobile Trade Association of Portugal (Associação do Comércio Automóvel de Portugal: ACAP), registrations fell by 17.5% year on year (y/y) to 15,209 units last month. Following earlier declines, registrations during the first seven months of the year are now down by 45.6% y/y at 80,057 units. The trade association added that light commercial vehicle (LCV) registrations dropped by 19.4% y/y to 2,529 units in July, meaning that the YTD figure is now down 36.1% y/y at 14,151 units. However, medium and heavy commercial vehicle (MHCV) registrations have surged in July by 67.3% y/y to 363 units, with the YTD figure now down 42.5% y/y at 1,894 units. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Ian Fletcher)
- Bayer's EBITDA before special items rose by 5.6% year on year
(YOY) in the second quarter to €2.88 billion, net of €12 million in
negative currency effects, beating analysts' consensus estimate by
5%. (IHS Markit Chemical's Ian Young)
- Sales declined by 2.5% on a currency- and portfolio-adjusted basis to €10.05 billion and the special charges drove EBIT down to a negative €10.78 billion from a positive €785 million in the year-earlier period.
- Bayer, meanwhile, has downgraded its full-year outlook due to the impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic.
- Free cash flow amounted to €1.40 billion in the second quarter, up from €751 million a year earlier.
- Net debt increased by 1.7% compared with 31 March 2020, to €35.99 billion as of 30 June 2020.
- The company says that the total costs to settle the approximately 125,000 filed and unfiled glyphosate claims and support a class settlement agreement to manage and resolve potential future litigation are currently expected to be up to $10.9 billion.
- Bayer raised second-quarter sales at Crop Science, its agricultural business, by 3.2% YOY to €4.80 billion, with the Latin America, APAC, and North America regions contributing to the increase.
- Sales at Bayer's pharmaceuticals business declined 8.8% YOY to €3.99 billion. The company cites contact restrictions and protective measures introduced worldwide due to the COVID-19 pandemic that led to a drop in elective treatments in doctors' offices and hospitals, with some treatments being postponed. EBITDA before special items at pharmaceuticals decreased by 7.1% YOY to €1.37 billion, primarily as a result of the decline in sales.
- Sales at the consumer health business declined by 1.9% YOY to €1.20 billion on destocking by retailers and consumers, as well as quarantine and protective measures introduced in various regions leading to less in-store retail traffic. EBITDA before special items at consumer health declined 10.9% to €254 million, primarily due to lower volumes as a result of COVID-19 and divestments.
- Bayer says it has downgraded its full-year guidance, made in February, because the financial impact of the COVID-19 pandemic remains difficult to predict. Bayer now forecasts currency-adjusted 2020 sales of €43-44 billion, down from previous guidance of €44-45 billion, or an increase of 0-1% compared with a previous forecast for growth of about 3-4% on a currency- and portfolio-adjusted basis.
- Tesla is on track for a quick build program on its new German facility, according to the Economic Minister for Brandenburg Joerg Steinbach. The plant is being built in the state of Brandenburg and is near the site of Berlin's new international airport to facilitate easy travel access and freight logistics. Steinbach said, "The goal at Tesla seems to be to beat the construction time for the Gigafactory 3 in Shanghai. According to my observation, this could very well succeed." (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Tim Urquhart)
- Turkey's Automobile Joint Venture Group Inc (TOGG) has announced the signing of an agreement with Germany-based automotive engineering services provider FEV to collaborate on the production of a domestically made electric vehicle (EV) in Turkey, reports the Daily Sabah. Turkish Industry and Technology Minister Mustafa Varank said that "the government also sought to make the IT Valley a center for tech-based startups and had started to work on creating a USD100 million (TRY700 million) Venture Capital Investment Fund". He added, "We want to support projects in areas such as transportation, communication, IoT [Internet of Things], finance, cybersecurity, robotics and automation with this fund." (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Tarun Thakur)
Asia-Pacific
- APAC equity markets closed higher across the region; India/Hong Kong +2.0%, Australia +1.9%, Japan +1.7%, South Korea +1.3%, and China +0.1%.
- China's proposed expansion of infrastructure investment would
play a countercyclical role to stabilize domestic demand and help
cushion the external growth headwinds. In the long term, better
infrastructural connectivity would also drive mobility, and
potentially attract more talent and investment inflows to mainland
market. (IHS Markit Economist Lei Yi)
- Mainland China's National Development and Reform Commission (NDRC) approved the construction of a batch of inter-city railway projects worth CNY474.1 billion (USD 67.9 billion) in the Greater Bay Area on 3 August, with their length totaling 775 kilometers.
- The capital requirement (as initial investment) for these projects was set at 50% by the NDRC and will be funded by local governments of cities along the railways. The remainder half can be raised through bank loans or other funding sources.
- The NDRC did not specify a detailed completion timeline for these projects, only stating that the construction work of several projects (totaling 337 kilometers) will be launched before 2022, and the rest will be started when construction conditions are ready.
- Approved projects would boost infrastructure investment in the Greater Bay Area and act as a countercyclical tool to stabilize domestic demand.
- Bank of India released its June 2020 financial results on 3
August. According to the financial reports, the bank's
non-performing loan ratio fell from 14.8% in the March quarter to
13.9% in the June quarter. (IHS Markit Banking Risk's Angus Lam)
- The bank's return on average asset returned positive to 0.5% from -2.0% in the previous quarter.
- The bank's capital adequacy ratio dipped slightly from 13.1% to 12.8%, and its tier-1 ratio fell from 9.9% to 9.5%.
- At its press conference, the bank's chief executive AK Das noted that the bank will raise INR70-80 billion (USD930 million to USD1.1 billion) of capital from equity and bonds by the December quarter to supports its credit growth of 7%.
- IHS Markit expects the government to inject capital into banks following the stress-test result released in the recent financial stability report; Bank of India is unlikely to be one of the five banks that is likely to face capital issues.
- Since Bank of India's financial results are healthy, it is likely to be able to raise funds from markets, just as some other Indian banks have done recently, while reserving fire power for weaker banks.
- However, in our view, the bank's asset quality and provisioning, the latter of which fell from INR73.1 billion in the March quarter of 2020 to INR7.7 billion in the June quarter, supporting profitability, are likely to be supported by the loan moratorium that is due to end at end-August.
- Tata Motors reported a consolidated net loss of INR84.3 billion
(USD1.1 billion) for the first quarter of fiscal year (FY) 2020/21
ended 30 June 2020, compared to INR36.8 billion net loss in the
same period of FY 2019/20. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Isha
Sharma)
- According to a filing by the company with the Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE), consolidated revenues from operations during the first quarter of the current FY declined by 48% year on year (y/y) to INR319.8 billion as COVID-19 virus continued to affect production and sales.
- Jaguar Land Rover (JLR) was once again the biggest contributor to Tata's top line in the first quarter. However, the luxury unit made a GBP648-million (USD846.5-million) net loss.
- The company incurred a tax charge of GBP235 million in the first quarter as a result of the Group's inability to fully recognize all deferred tax assets on the balance sheet, resulting in no tax credit on current period losses and an income statement tax charge due to the movement in the pension obligation.
- Sales revenues were down 44% y/y to GBP2.8 billion. During the three-month period, JLR's retail sales declined 42.4% y/y to 74,067 vehicles due to the negative impact of the COVID-19 virus pandemic, with China sales down only 2.5% y/y as social distancing measures eased there.
- Tata Motors' standalone business posted a net loss of INR21.9 billion for the quarter, compared to a net loss of INR971 million in the corresponding quarter of last FY.
- Tata Motors standalone revenues from operations were down 80% y/y to INR26.8 billion.
- During the period, Tata Motors wholesales (including exports) slumped 81.5% to 25,294 units. In the domestic market, medium and commercial vehicle (MHCV) sales declined 92.1% y/y, intermediate and light commercial vehicle (ILCV) sales declined 92.1% y/y, small commercial vehicles (SCVs) and pick-ups sales decreased 85.4% y/y.
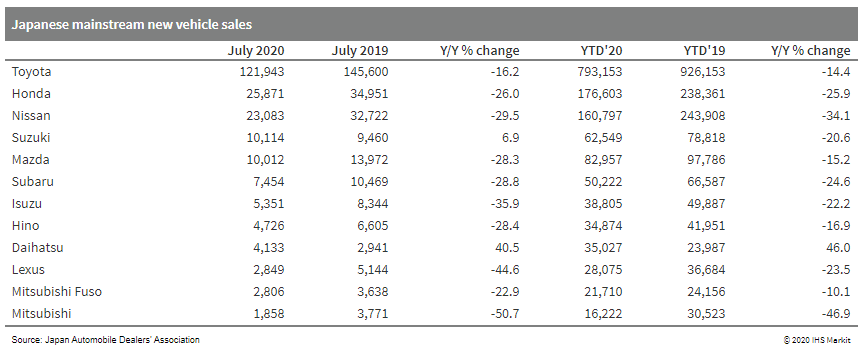
- Japanese new vehicle sales, including mainstream and
mini-vehicles, were down by 13.7% year on year (y/y) in July to
396,346 units. In the year to date (YTD), sales declined by 18.9%
y/y to 2.604 million units. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Nitin
Budhiraja)
- Japanese sales of mainstream registered vehicles were 239,355 units, down by 20.4% y/y during July, according to data released by the Japan Automobile Dealers Association (JADA). This figure excludes mini-vehicles, thus covering all vehicles with engines greater than 660cc, including both passenger vehicles and commercial vehicles (CVs), sold in Japan.
- Of this total, sales of passenger and compact cars declined by 19.6% y/y to 207,473 units in July, while truck sales were down by 24.9% y/y to 31,176 units and bus sales by 37.9% y/y to 706 units.
- In the YTD, sales of mainstream registered vehicles declined by
19.5% y/y to 1.639 million units. Sales of passenger cars were down
by 19.9% y/y at 1.405 million units, while truck sales fell by
17.1% y/y to 226,601 units and bus sales shrank by 22.9% y/y to
6,551 units.
- The Seoul city government has unveiled a 'No Diesel' initiative aimed at eliminating high emitting vehicles from the roads and replacing them with electric and fuel-cell powered vehicles, reports The Korea Herald. The new policy focuses on replacing diesel vehicles from public-sector and mass transit fleets with alternative-powertrain vehicles by 2025. Out of 5,153 diesel vehicles currently used in the public sector, around 3,586 vehicles will be replaced with electric and fuel-cell vehicles in stages by 2025. The city government will also remove diesel vehicles from public transportation, including taxis, airport buses, and city tour buses. The city, which already replaced all diesel buses with compressed natural gas (CNG) buses in 2015, also plans to introduce about 4,000 electric and fuel-cell buses by 2025. The city government also seeks to replace 30% of community buses with electric vehicles by 2023 and encourage school bus operators and car rental services to adopt alternative-powertrain vehicles. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Jamal Amir)
- Ride-hailing company Grab has raised USD200 million in funding from South Korean private equity firm STIC Investments, reports Bloomberg. STIC Investments will source USD100 million from one of its funds while the remainder will be raised from its co-investors. This latest development comes at a time when ride-hailing services have been hit by COVID-19 virus pandemic-related lockdowns globally. Recently, Grab laid off 360 employees, representing 5% of its total workforce, owing to the pandemic. It has raised more than USD10 billion to date including its latest USD856 million funding from Japanese investors. The company is currently working on transforming itself from a traditional taxi-booking firm into a consumer technology group and is offering a range of services, including finance, payments, and rides. Grab's app has been downloaded on 166 million devices and processes more than 6 million ride orders per day. (IHS Markit Automotive Mobility's Surabhi Rajpal)
As per IHS Markit's Commodities at Sea (CAS), the arrival of iron ore and bauxite vessels at the Chinese ports in July 2020 was quite strong at 111.6mt (up 15% m-o-m and 21% y-o-y) and 10.5mt (up 14% m-o-m and up to 28% y-o-y), respectively. The latest PMI manufacturing data also signaled the same trend and highlighted the quickest expansions of output and new orders since January 2011 amid reports of firmer customer demand. Caixin China General Manufacturing PMI for July 2020 was announced at 52.8 from 51.2 a month before. The gauge for stocks of finished goods stood slightly below 50, and the gauge for backlogs of work continued to expand, reflecting strong demand. Arrivals of both iron ore and bauxite were quite strong during July 2020; however, coal shipments slowed down to 20.4mt (down 19% m-o-m and down 17% y-o-y). Slower arrivals of coal shipments were on the back of prevailing restrictive import quotas, lesser demand on the back of heavy rains in various parts of the country as well as improving domestic coal production. Imported coal arrivals are expected to not remain strong in anticipation that small coal mines in the Inner Mongolia which were suspended would resume mining activities as they have received August sales licenses. As per IHS McCloskey, Inner Mongolia has been asked to raise output by 10%, which could lead to a relaxing of the region's sales control policies, while Shaanxi, where the one-month safety campaign ended at end-June, is also expected to reopen some of the suspended small mines. (IHS Markit Maritime and Trade's Rahul Kapoor and Pranay Shukla)
S&P Global provides industry-leading data, software and technology platforms and managed services to tackle some of the most difficult challenges in financial markets. We help our customers better understand complicated markets, reduce risk, operate more efficiently and comply with financial regulation.
This article was published by S&P Global Market Intelligence and not by S&P Global Ratings, which is a separately managed division of S&P Global.
