Published September 2021
Only three of the many possible products resulting from the chlorination of benzene continue to have any large-volume applications—monochlorobenzene, o-dichlorobenzene, and p-dichlorobenzene—combined they account for about 96.5% of the total chlorobenzenes market. Other chlorobenzenes that have commercial applications but are not produced on a large scale include m-dichlorobenzene, trichlorobenzenes, tetrachlorobenzenes, and hexachlorobenzene. Market information on these products is included in the report where available.
The following pie chart shows consumption of chlorobenzenes in the major regions in 2021:
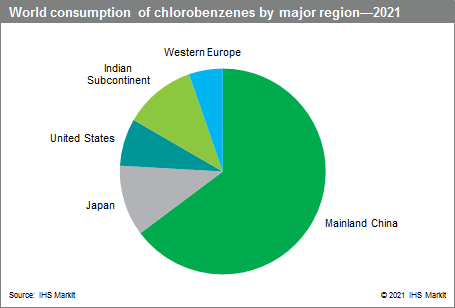
Mainland China is still the world’s largest consumer of chlorobenzenes, but the consumption share has declined slightly. Consumption in Western Europe and the United States have declined by 2–3% from 2016 levels, while Japan’s share has increased slightly. The Indian Subcontinent is the only region in which its share has increased significantly, growing by more than 3% from 2016 level.
Mononchlorobenzene still accounts for the largest share of chlorobenzene consumption, corresponding to more than half of the global total; however, this share was close to three-quarters in 2016.
Nitrochlorobenzene is the most significant end use for monochlorobenzene, and is consumed as an intermediate in the manufacture of dyes and pigments, rubber-processing chemicals, pesticides, pharmaceuticals, and other organic chemicals.
o-Dichlorobenzene is a chemical intermediate consumed mostly for 3,4-dichloroaniline in the United States, South America, and Western Europe; as an herbicide intermediate in Japan; and for pesticides and pharmaceuticals in mainland China and the Indian Subcontinent.
Worldwide, p-dichlorobenzene is used primarily as a raw material for polyphenylene sulfide (PPS) resins, for deodorant blocks for indoor air, and for moth control. Polyphenylene sulfide resin is a growing highperformance engineering resin that is produced only in the United States, Japan, mainland China, and since mid-2016, South Korea.
Compared to 2016 levels, consumption of monochlorobenzene has contracted in 2021 while consumption of ortho- and para- dichlorobenzenes have increased by double-digit rates; consumption of other chlorobenzenes has increased more than 1.5 times. Healthy growth of pharmaceuticals and TDI, and fast growth of polyphenylene sulfide resins have driving consumption of o-dichlorobenzene and p-dichlorobenzene constantly over the last several years. Between 2016 and 2021, the impact of weakened demand, environmental restrictions, and the economic recession during the pandemic have slowed global consumption.
Between 2021 and 2026, monochlorobenzene consumption is anticipated to growth at a healthy rate owing to consumption recovery in mainland China and consumption growth in the Indian Subcontinent. Consumption of o-dichlorobenzene and p-dichlorobenzene is expected to experience healthy growth as well, driven by positive demand of diverse end uses.
Anticipating a global economic recovery to pre-COVID levels in the near future, global chlorobenzene consumption is expected to grow at a healthy rate over the next few years.
For more detailed information, see the table of contents, shown below.
S&P Global’s Chemical Economics Handbook – Chlorobenzenes is the comprehensive and trusted guide for anyone seeking information on this industry. This latest report details global and regional information, including
Key Benefits
S&P Global’s Chemical Economics Handbook – Chlorobenzenes has been compiled using primary interviews with key suppliers and organizations, and leading representatives from the industry in combination with S&P Global’s unparalleled access to upstream and downstream market intelligence and expert insights into industry dynamics, trade, and economics.
This report can help you
- Identify trends and driving forces influencing chemical markets
- Forecast and plan for future demand
- Understand the impact of competing materials
- Identify and evaluate potential customers and competitors
- Evaluate producers
- Track changing prices and trade movements
- Analyze the impact of feedstocks, regulations, and other factors on chemical profitability

















